PaddleX Text Detection/Text Recognition Task Module Data Annotation Tutorial¶
1. Annotation Data Examples¶
2. PPOCRLabel Annotation¶
2.1 Introduction to PPOCRLabel Annotation Tool¶
PPOCRLabel is a semi-automatic graphical annotation tool tailored for OCR tasks, featuring automatic annotation and re-recognition of data using the built-in PP-OCR model. Written in Python3 and PyQT5, it supports rectangular box annotation, table annotation, irregular text annotation, and key information annotation modes. In OCR annotation tasks, labels are stored as txt files.
2.2 Installation and Running PPOCRLabel¶
PPOCRLabel can be launched through whl packages or Python scripts. The whl package method is more convenient, and only this method is provided here:
- For Windows:
[!NOTE] Installing PPOCRLabel via whl packages will automatically download the
paddleocrwhl package. The shapely dependency may encounter a "[winRrror 126] The specified module could not be found." error. It is recommended to download and install the shapely installation package separately.
- For MacOS:
2.3 Annotation Process for Text Detection and Text Recognition¶
- Installation and Running: Use the above commands to install and run the program.
- Open Folder: Click "File" - "Open Directory" to select the folder containing images to be annotated.
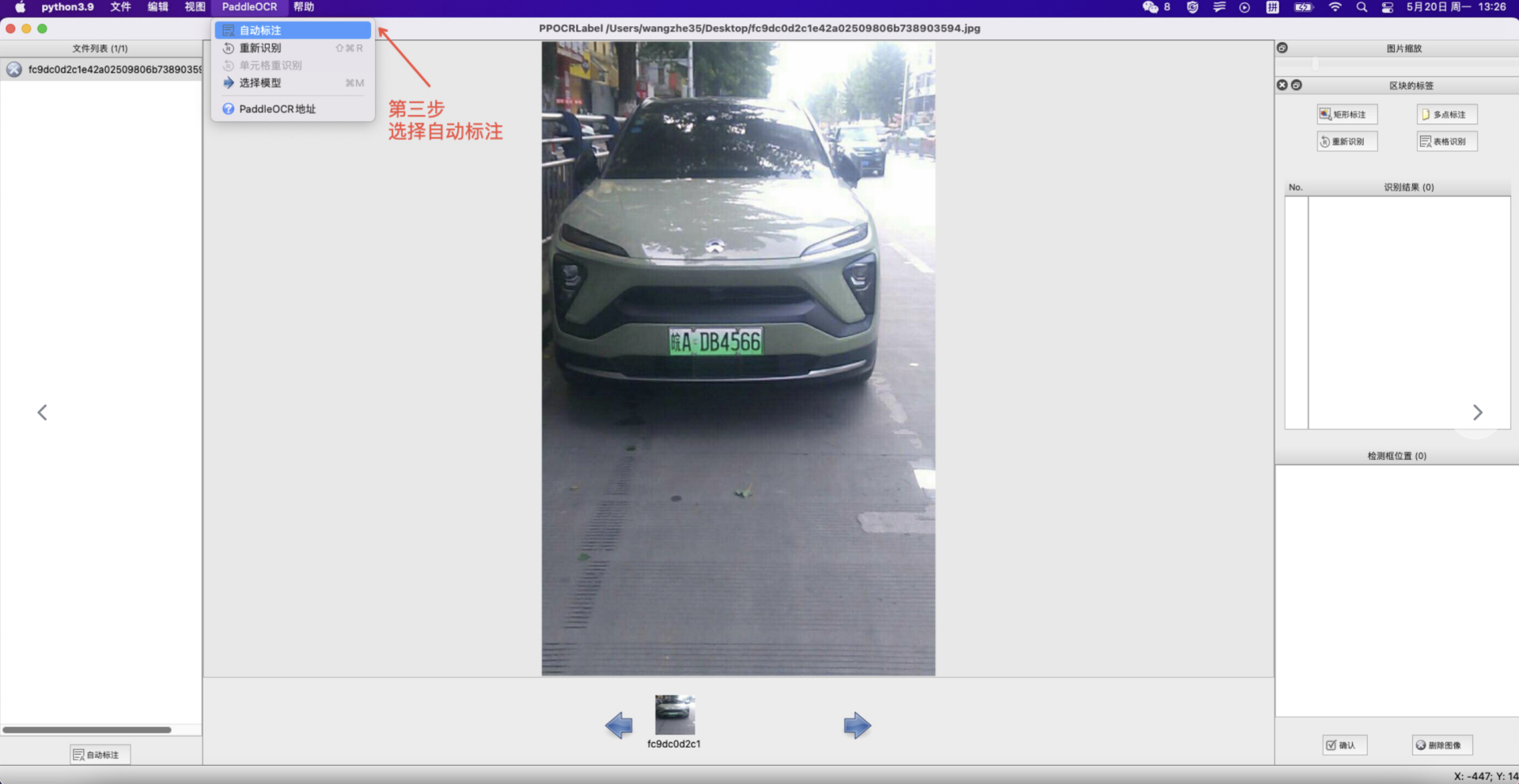
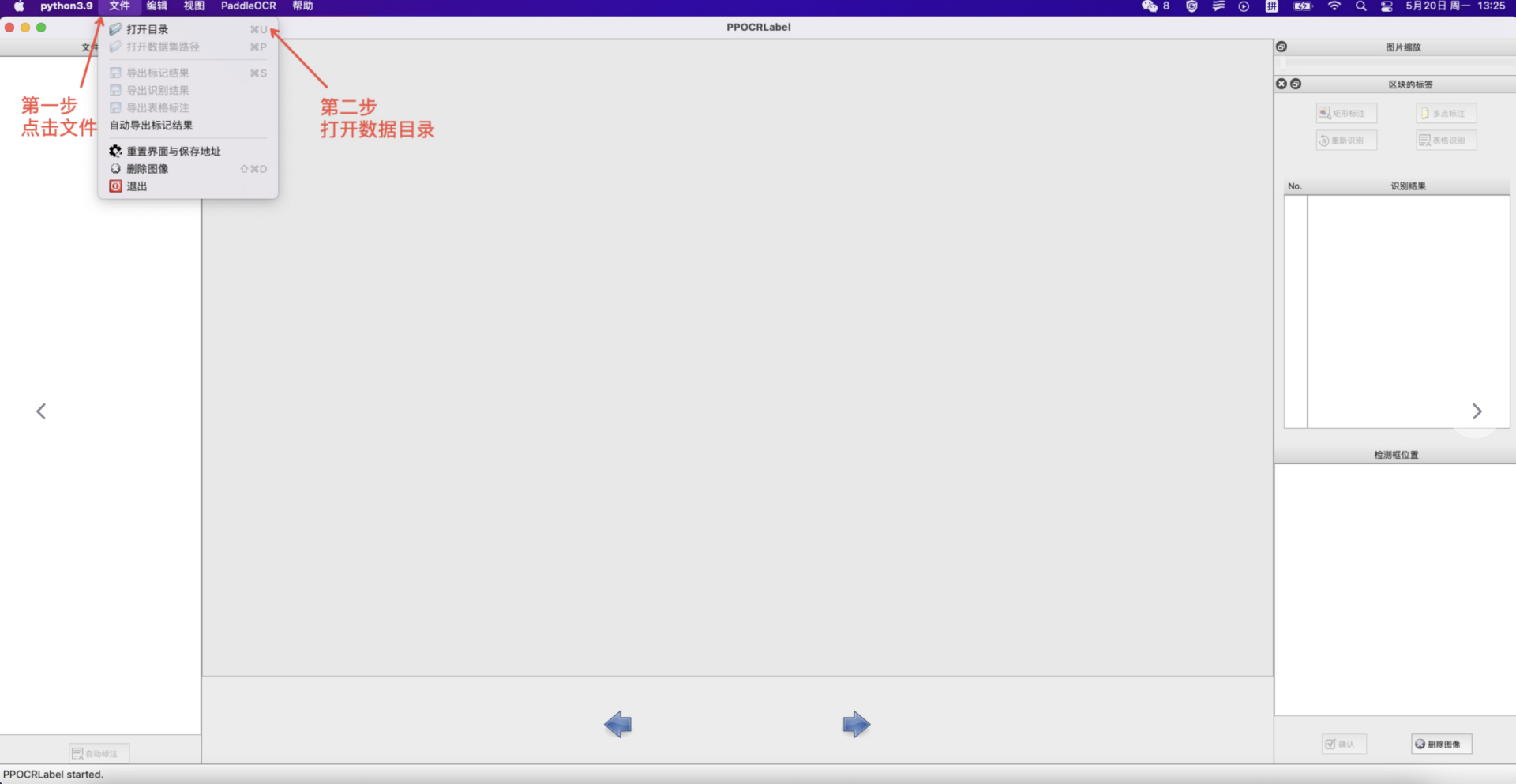 3. Auto Annotation: Click "Auto Annotation" to use the PP-OCR ultra-lightweight model to automatically annotate images with a file status of "X".
3. Auto Annotation: Click "Auto Annotation" to use the PP-OCR ultra-lightweight model to automatically annotate images with a file status of "X".
 4. Manual Annotation: Click "Rectangle Annotation" (recommended to press "W" directly in English mode), and users can manually draw bounding boxes for parts undetected by the model in the current image. Press "Q" on the keyboard to use the four-point annotation mode (or click "Edit" - "Four-point Annotation"), and users click 4 points in sequence, double-clicking the left mouse button to indicate completion.
5. After drawing the bounding box, click "Confirm", and the detection box will be pre-assigned a "To Be Recognized" label.
6. Re-Recognition: After drawing/adjusting all detection boxes in the image, click "Re-Recognition", and the PP-OCR model will re-recognize all detection boxes in the current image.
4. Manual Annotation: Click "Rectangle Annotation" (recommended to press "W" directly in English mode), and users can manually draw bounding boxes for parts undetected by the model in the current image. Press "Q" on the keyboard to use the four-point annotation mode (or click "Edit" - "Four-point Annotation"), and users click 4 points in sequence, double-clicking the left mouse button to indicate completion.
5. After drawing the bounding box, click "Confirm", and the detection box will be pre-assigned a "To Be Recognized" label.
6. Re-Recognition: After drawing/adjusting all detection boxes in the image, click "Re-Recognition", and the PP-OCR model will re-recognize all detection boxes in the current image.
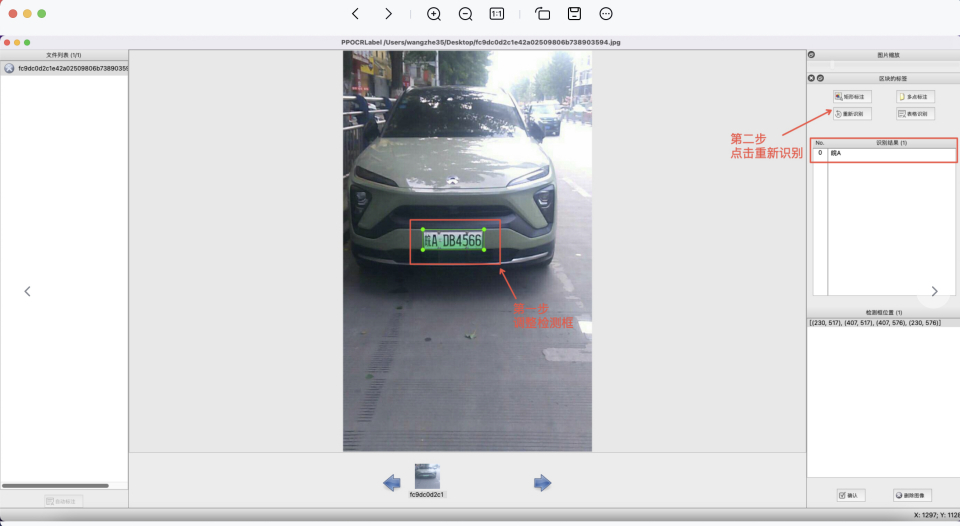
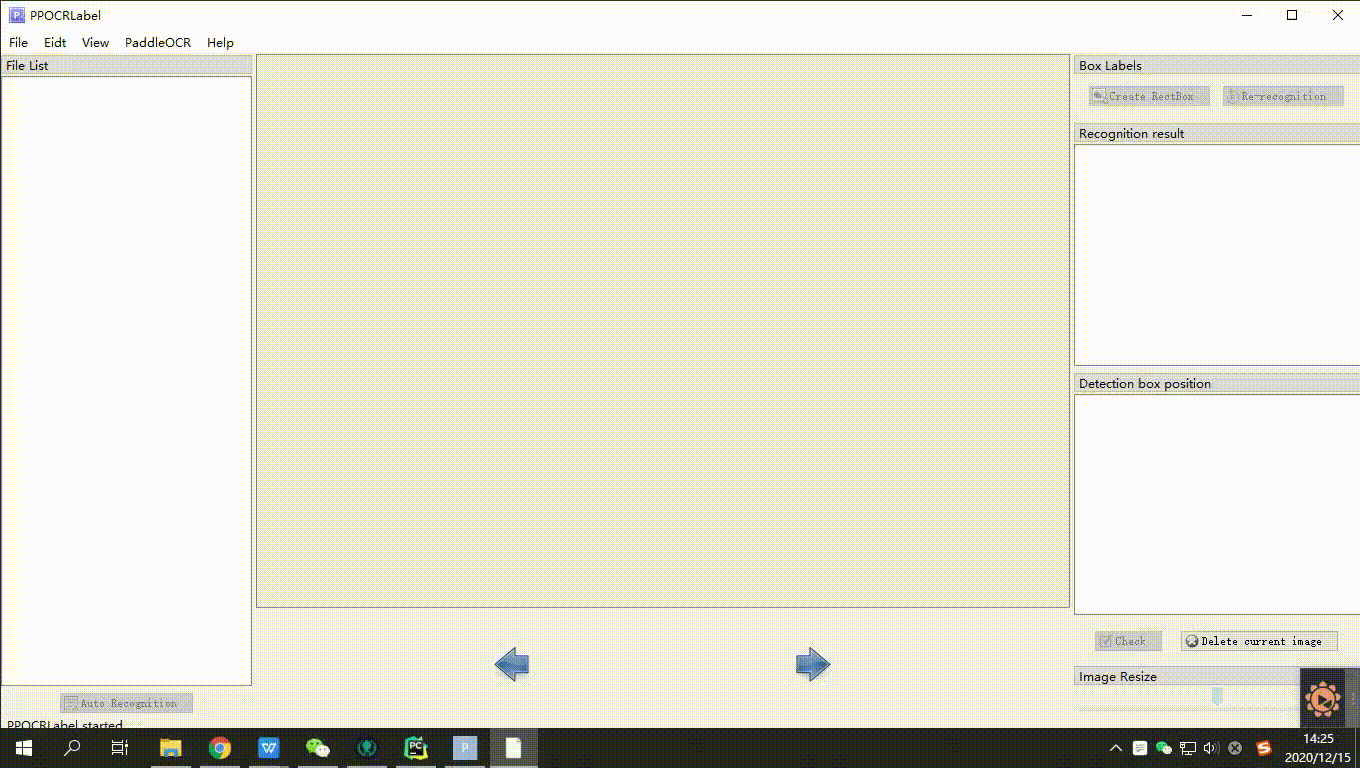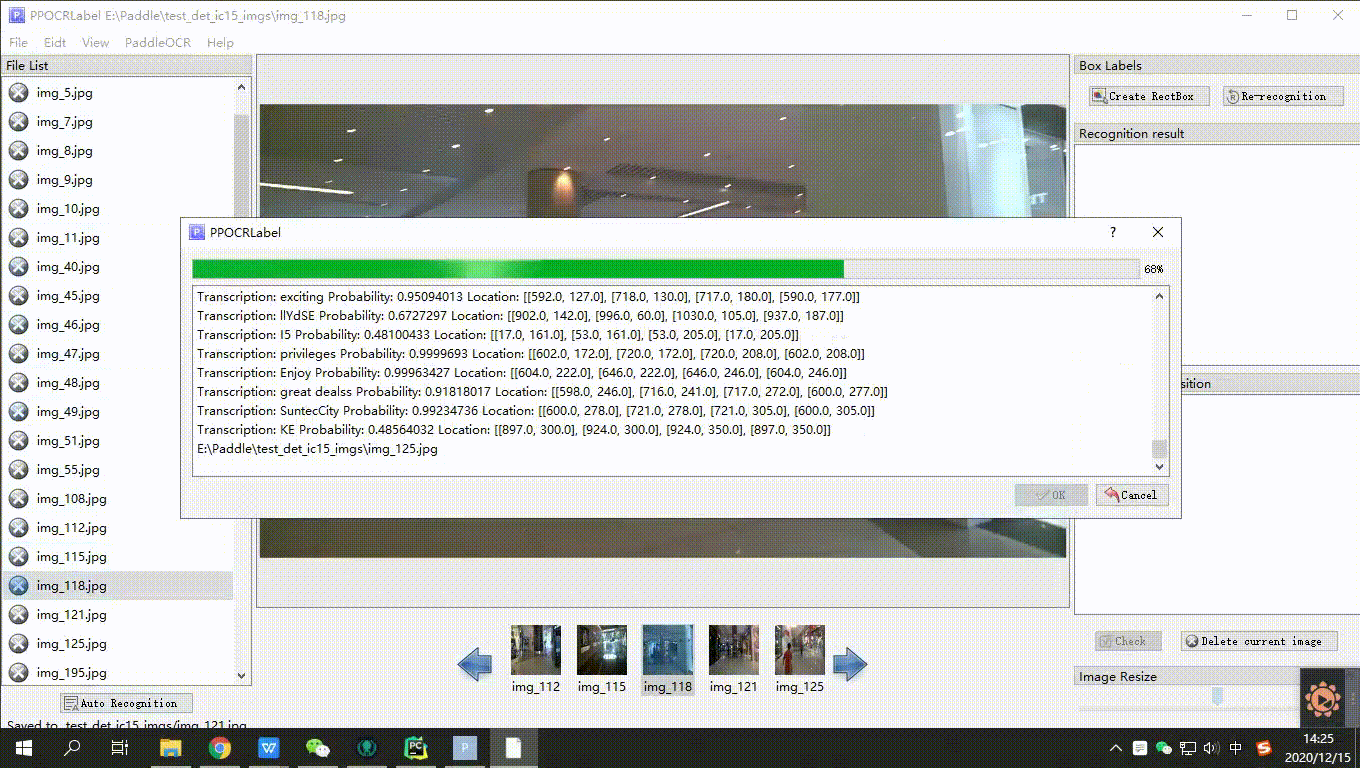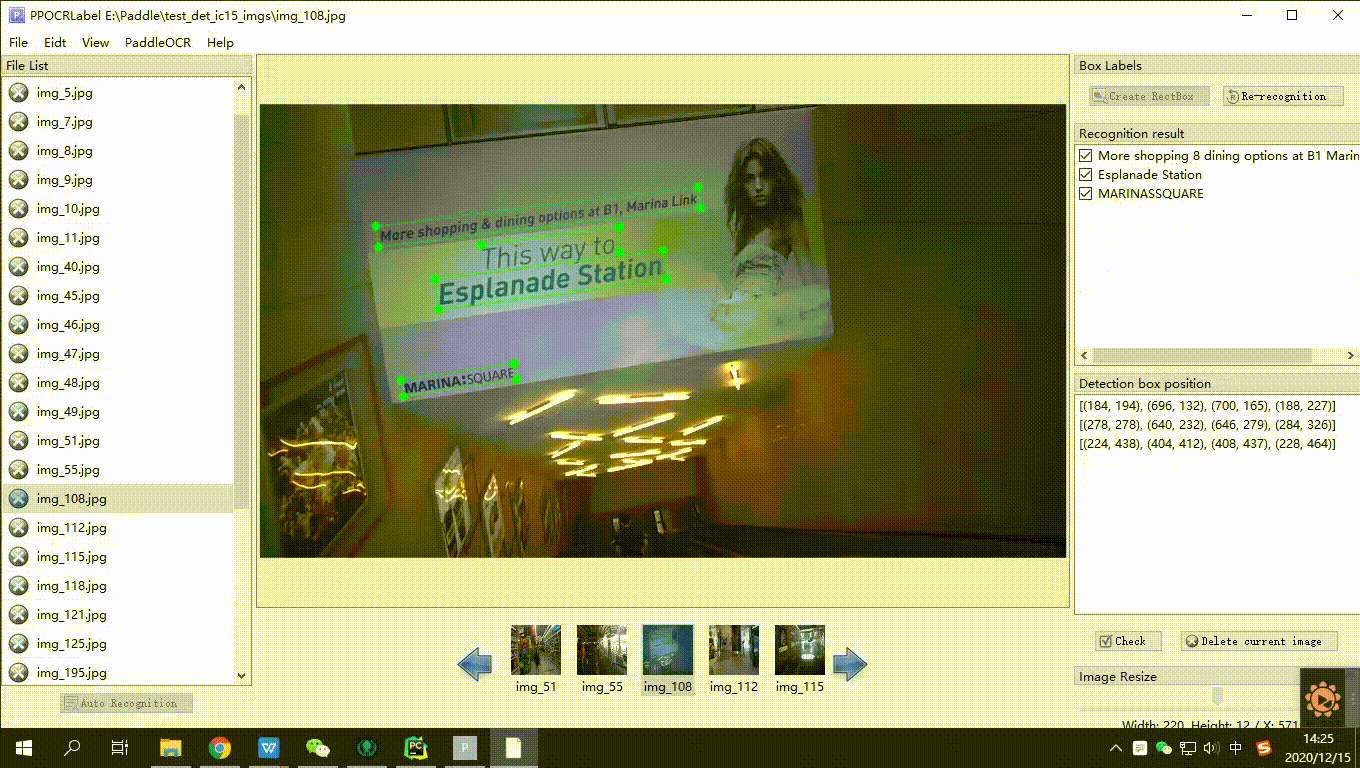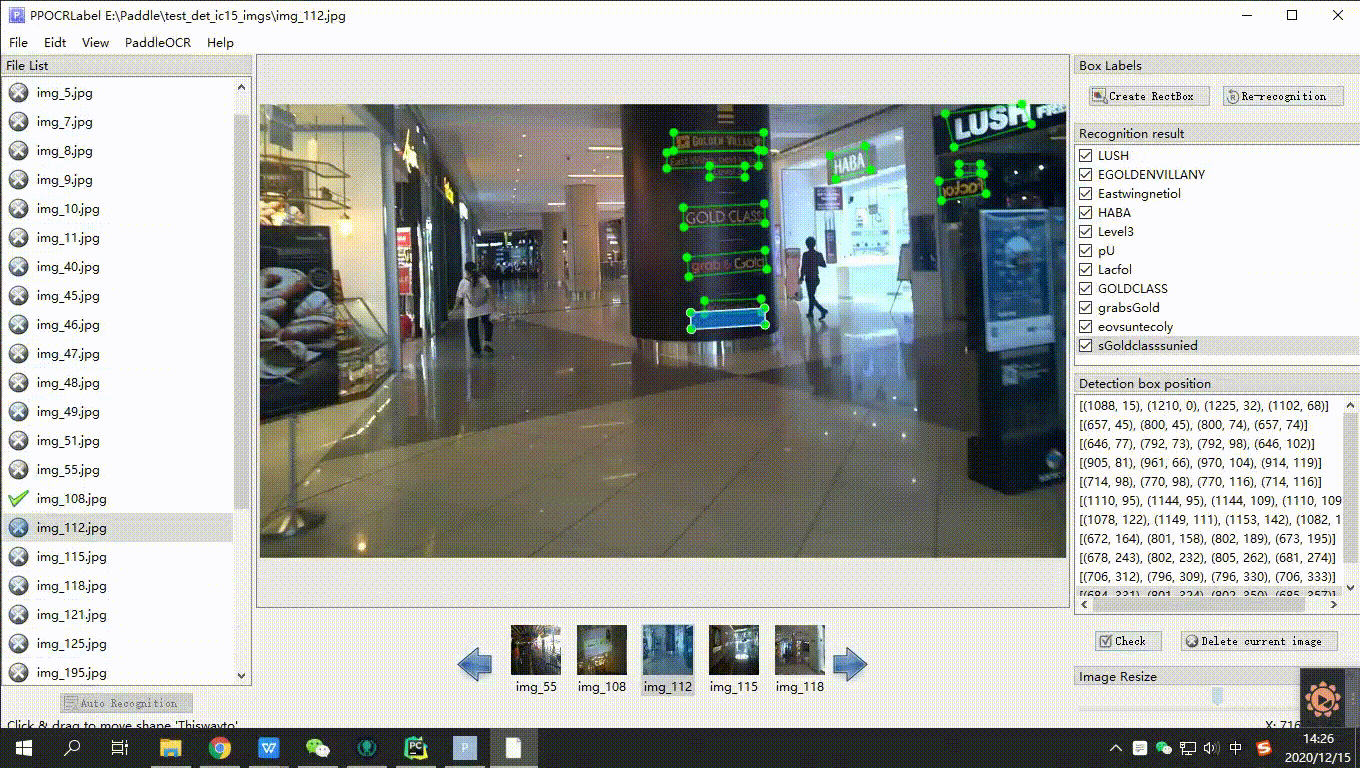
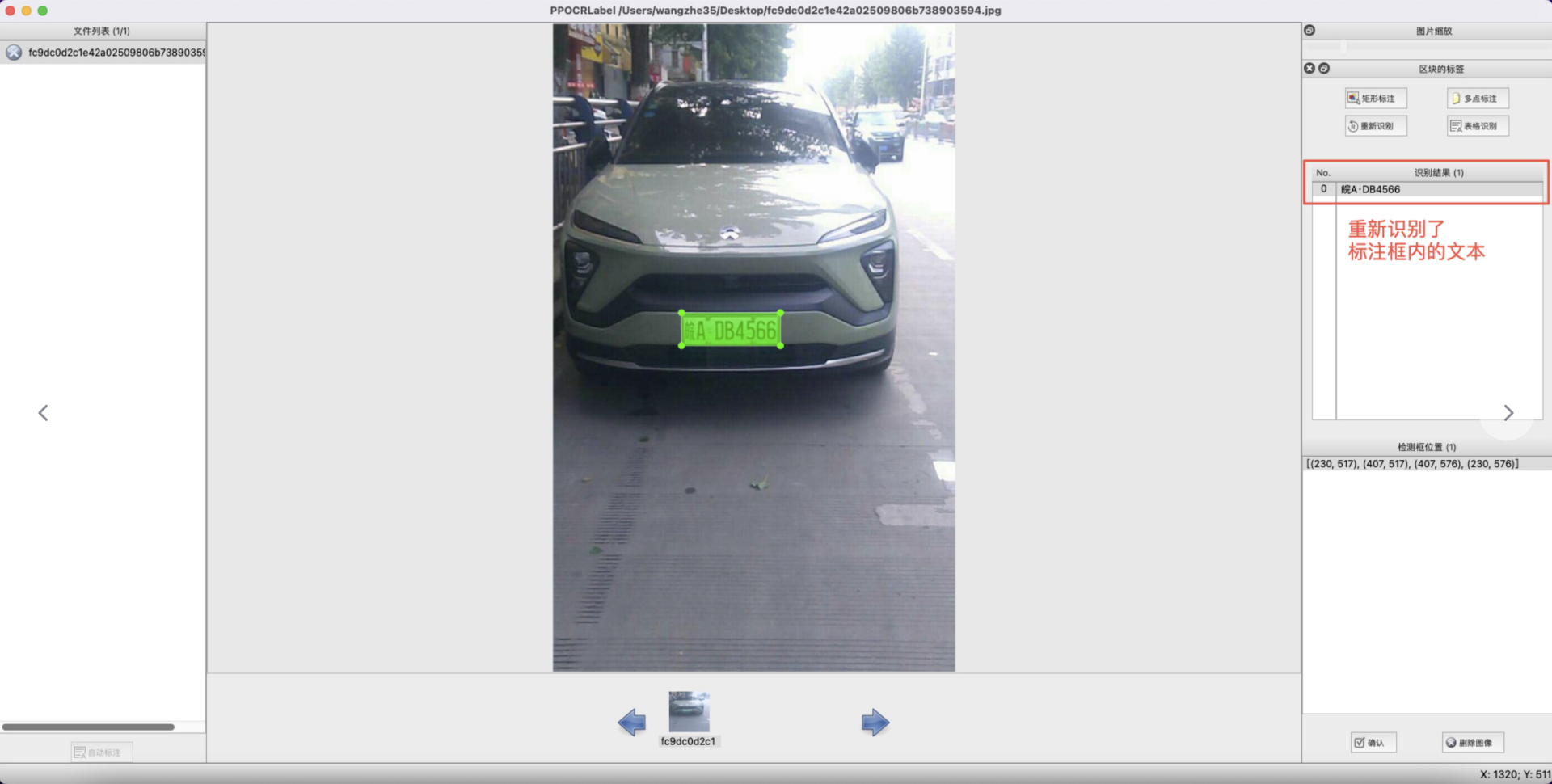 7. Content Modification: Click on the recognition result to manually modify inaccurate recognition results.
8. Confirm Annotation: Click "Confirm", the image status changes to "√", and proceed to the next image.
9. Deletion: Click "Delete Image", and the image will be deleted to the Recycle Bin.
10. Export Results: Users can manually export results through "File - Export Annotation Results" or enable automatic export by clicking "File - Auto Export Annotation Results". Manually confirmed annotations will be stored in
7. Content Modification: Click on the recognition result to manually modify inaccurate recognition results.
8. Confirm Annotation: Click "Confirm", the image status changes to "√", and proceed to the next image.
9. Deletion: Click "Delete Image", and the image will be deleted to the Recycle Bin.
10. Export Results: Users can manually export results through "File - Export Annotation Results" or enable automatic export by clicking "File - Auto Export Annotation Results". Manually confirmed annotations will be stored in Label.txt under the opened image folder. Clicking "File - Export Recognition Results" in the menu bar will save the recognition training data of such images in the crop_img folder, and the recognition labels will be saved in rec_gt.txt.
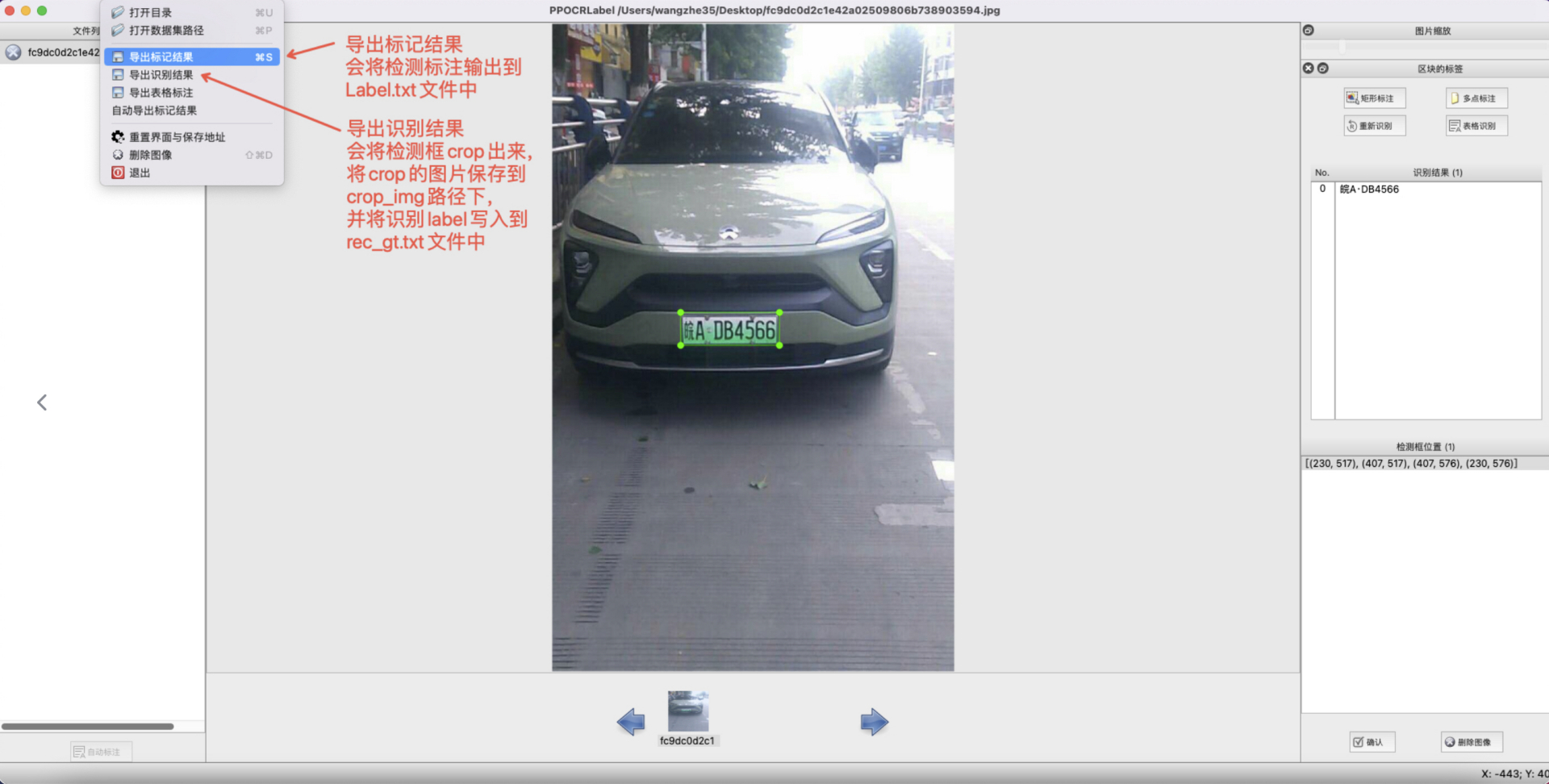 Notes:
Notes:
- PPOCRLabel uses folders as the basic unit for labeling. After opening the folder containing images to be labeled, the images will not be displayed in the window bar. Instead, clicking "Select Folder" will directly import the images under the folder into the program.
- The image status indicates whether the current image has been manually saved by the user. An "X" indicates it has not been manually saved, while a "√" indicates it has. After clicking the "Auto Label" button, PPOCRLabel will not relabel images with a status of "√".
- Clicking "Re-recognize" will overwrite the recognition results in the image. Therefore, if manual changes have been made to the recognition results before this, they may be altered after re-recognition.
- Files generated by PPOCRLabel are placed in the folder containing the labeled images, including the following types. Do not manually modify their contents as it may cause program exceptions.
| File Name | Description |
|---|---|
Label.txt |
Detection labels, which can be directly used for PPOCR detection model training. The program automatically writes to this file every 5 confirmed detection results, or when the application is closed or the file path is changed. |
fileState.txt |
Image status marker file, which saves the names of images in the current folder that have been manually confirmed by the user. |
Cache.cach |
Cache file, which saves the results of automatic recognition by the model. |
rec_gt.txt |
Recognition labels. Can be directly used for PPOCR recognition model training. Generated by manually clicking "Export Recognition Results" in the menu bar. |
crop_img |
Recognition data. Images cropped according to the detection boxes. Generated simultaneously with rec_gt.txt. |
If data partitioning is required, follow these steps:
cd ./PPOCRLabel # Switch to the PPOCRLabel folder
python gen_ocr_train_val_test.py --trainValTestRatio 7:3:0 --datasetRootPath ../train_data
trainValTestRatio is the ratio for dividing images into training, validation, and test sets. Set it according to your needs. The default is 6:2:2.
* datasetRootPath is the full path to the dataset labeled by PPOCRLabel. The default path is PaddleOCR/train_data. Before partitioning the dataset, the structure should be as follows:
|-train_data
|-crop_img
|- word_001_crop_0.png
|- word_002_crop_0.jpg
|- word_003_crop_0.jpg
| ...
| Label.txt
| rec_gt.txt
|- word_001.png
|- word_002.jpg
|- word_003.jpg
| ...
3. Data Format¶
PaddleX defines a dataset named TextDetDataset specifically for text detection tasks. The organized and annotated data should follow the following file organization and naming conventions:
dataset_dir # Root directory of the dataset, the directory name can be changed
├── images # Directory to store images, the directory name can be changed but should correspond to the content in train.txt and val.txt
├── train.txt # Annotation file for the training set, the file name cannot be changed. Example content: images/img_0.jpg \t [{"transcription": "MASA", "points": [[310, 104], [416, 141], [418, 216], [312, 179]]}, {...}]
└── val.txt # Annotation file for the validation set, the file name cannot be changed. Example content: images/img_61.jpg \t [{"transcription": "TEXT", "points": [[31, 10], [310, 140], [420, 220], [310, 170]]}, {...}]
images directory, and rename the generated Label.txt annotation file to train.txt for the training set. Similarly, rename the Label.txt annotation file for the validation set to val.txt. Both files should be placed in the dataset_dir (the name of which can be changed) directory. Note that the image paths in train.txt/val.txt should be in the format images/xxx.
Each line in the annotation files contains the path to an image and a list of dictionaries. The path and the list must be separated by a tab character ‘\t’, not spaces.
For the list of dictionaries, the points key represents the coordinates (x, y) of the four vertices of the text box, starting from the top-left vertex and proceeding clockwise. The transcription key indicates the text within the text box. If the transcription content is "###", it indicates that the text box is invalid and will not be used for training. For reference, see the example dataset.
If you use PPOCRLabel to annotate your data, simply rename det_gt_train.txt in the text detection (det) directory to train.txt and det_gt_test.txt to val.txt after dividing your dataset.