Formula Recognition Pipeline Usage Tutorial¶
1. Introduction to Formula Recognition Pipeline¶
Formula recognition is a technology that automatically identifies and extracts LaTeX formula content and structure from documents or images. It is widely used in fields such as mathematics, physics, and computer science for document editing and data analysis. By using computer vision and machine learning algorithms, formula recognition can convert complex mathematical formula information into editable LaTeX format, facilitating further processing and analysis of data.
The formula recognition pipeline is designed to solve formula recognition tasks by extracting formula information from images and outputting it in LaTeX source code format. This pipeline integrates the advanced formula recognition model PP-FormulaNet developed by the PaddlePaddle Vision Team and the well-known formula recognition model UniMERNet. It is an end-to-end formula recognition system that supports the recognition of simple printed formulas, complex printed formulas, and handwritten formulas. Additionally, it includes functions for image orientation correction and distortion correction. Based on this pipeline, precise formula content prediction can be achieved, covering various application scenarios in education, research, finance, manufacturing, and other fields. The pipeline also provides flexible deployment options, supporting multiple hardware devices and programming languages. Moreover, it offers the capability for custom development. You can train and optimize the pipeline on your own dataset, and the trained model can be seamlessly integrated.

The formula recognition pipeline includes the following four modules. Each module can be trained and inferred independently and contains multiple models. For more details, please click on the respective module to view the documentation.
- Formula Recognition Module
- Layout Detection Module(Optional)
- Document Image Orientation Classification Module (Optional)
- Text Image Correction Module (Optional)
In this pipeline, you can choose the model you want to use based on the benchmark data provided below.
The inference time only includes the model inference time and does not include the time for pre- or post-processing.
Document Image Orientation Classification Module (Optional):
| Model | Model Download Link | Top-1 Acc (%) | GPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
CPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
Model Storage Size (MB) | Introduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP-LCNet_x1_0_doc_ori | Inference Model/Training Model | 99.06 | 2.62 / 0.59 | 3.24 / 1.19 | 7 | A document image classification model based on PP-LCNet_x1_0, with four categories: 0 degrees, 90 degrees, 180 degrees, and 270 degrees. |
Text Image Correction Module (Optional):
| Model | Model Download Link | CER | GPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
CPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
Model Storage Size (MB) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UVDoc | Inference Model/Training Model | 0.179 | 19.05 / 19.05 | - / 869.82 | 30.3 | High-precision text image correction model |
Layout Detection Module (Optional):
* The layout detection model includes 20 common categories: document title, paragraph title, text, page number, abstract, table, references, footnotes, header, footer, algorithm, formula, formula number, image, table, seal, figure_table title, chart, and sidebar text and lists of references| Model | Model Download Link | mAP(0.5) (%) | GPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
CPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
Model Storage Size (MB) | Introduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP-DocLayout_plus-L | Inference Model/Training Model | 83.2 | 53.03 / 17.23 | 634.62 / 378.32 | 126.01 | A higher-precision layout area localization model trained on a self-built dataset containing Chinese and English papers, PPT, multi-layout magazines, contracts, books, exams, ancient books and research reports using RT-DETR-L |
| Model | Model Download Link | mAP(0.5) (%) | GPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
CPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
Model Storage Size (MB) | Introduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP-DocLayout-L | Inference Model/Training Model | 90.4 | 33.59 / 33.59 | 503.01 / 251.08 | 123.76 | A high-precision layout area localization model trained on a self-built dataset containing Chinese and English papers, magazines, contracts, books, exams, and research reports using RT-DETR-L. |
| PP-DocLayout-M | Inference Model/Training Model | 75.2 | 13.03 / 4.72 | 43.39 / 24.44 | 22.578 | A layout area localization model with balanced precision and efficiency, trained on a self-built dataset containing Chinese and English papers, magazines, contracts, books, exams, and research reports using PicoDet-L. |
| PP-DocLayout-S | Inference Model/Training Model | 70.9 | 11.54 / 3.86 | 18.53 / 6.29 | 4.834 | A high-efficiency layout area localization model trained on a self-built dataset containing Chinese and English papers, magazines, contracts, books, exams, and research reports using PicoDet-S. |
👉Details of Model List
* Layout Detection Model, including 17 common layout categories: Paragraph Title, Image, Text, Number, Abstract, Content, Figure Caption, Formula, Table, Table Caption, References, Document Title, Footnote, Header, Algorithm, Footer, and Stamp| Model | Model Download Link | mAP(0.5) (%) | GPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
CPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
Model Storage Size (MB) | Introduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PicoDet-S_layout_17cls | Inference Model/Training Model | 87.4 | 8.80 / 3.62 | 17.51 / 6.35 | 4.8 | A high-efficiency layout area localization model trained on a self-built dataset of Chinese and English papers, magazines, and research reports using PicoDet-S. |
| PicoDet-L_layout_17cls | Inference Model/Training Model | 89.0 | 12.60 / 10.27 | 43.70 / 24.42 | 22.6 | A balanced efficiency and precision layout area localization model trained on a self-built dataset of Chinese and English papers, magazines, and research reports using PicoDet-L. |
| RT-DETR-H_layout_17cls | Inference Model/Training Model | 98.3 | 115.29 / 101.18 | 964.75 / 964.75 | 470.2 | A high-precision layout area localization model trained on a self-built dataset of Chinese and English papers, magazines, and research reports using RT-DETR-H. |
| Model | Model Download Link | mAP(0.5) (%) | GPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
CPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
Model Storage Size (MB) | Introduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP-DocLayout-L | Inference Model/Training Model | 90.4 | 33.59 / 33.59 | 503.01 / 251.08 | 123.76 | A high-precision layout area localization model trained on a self-built dataset containing Chinese and English papers, magazines, contracts, books, exams, and research reports using RT-DETR-L. |
| PP-DocLayout-M | Inference Model/Training Model | 75.2 | 13.03 / 4.72 | 43.39 / 24.44 | 22.578 | A layout area localization model with balanced precision and efficiency, trained on a self-built dataset containing Chinese and English papers, magazines, contracts, books, exams, and research reports using PicoDet-L. |
| PP-DocLayout-S | Inference Model/Training Model | 70.9 | 11.54 / 3.86 | 18.53 / 6.29 | 4.834 | A high-efficiency layout area localization model trained on a self-built dataset containing Chinese and English papers, magazines, contracts, books, exams, and research reports using PicoDet-S. |
| Model | Model Download Link | mAP(0.5) (%) | GPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
CPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
Model Storage Size (MB) | Introduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP-DocLayout_plus-L | Inference Model/Training Model | 83.2 | 53.03 / 17.23 | 634.62 / 378.32 | 126.01 | A higher-precision layout area localization model trained on a self-built dataset containing Chinese and English papers, PPT, multi-layout magazines, contracts, books, exams, ancient books and research reports using RT-DETR-L |
Formula Recognition Module :
| Model | Model Download Link | En-BLEU(%) | Zh-BLEU(%) | GPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
CPU Inference Time (ms) [Normal Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
Model Storage Size (MB) | Introduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UniMERNet | Inference Model/Training Model | 85.91 | 43.50 | 1311.84 / 1311.84 | - / 8288.07 | 1530 | UniMERNet is a formula recognition model developed by Shanghai AI Lab. It uses Donut Swin as the encoder and MBartDecoder as the decoder. The model is trained on a dataset of one million samples, including simple formulas, complex formulas, scanned formulas, and handwritten formulas, significantly improving the recognition accuracy of real-world formulas. |
| PP-FormulaNet-S | Inference Model/Training Model | 87.00 | 45.71 | 182.25 / 182.25 | - / 254.39 | 224 | PP-FormulaNet is an advanced formula recognition model developed by the Baidu PaddlePaddle Vision Team. The PP-FormulaNet-S version uses PP-HGNetV2-B4 as its backbone network. Through parallel masking and model distillation techniques, it significantly improves inference speed while maintaining high recognition accuracy, making it suitable for applications requiring fast inference. The PP-FormulaNet-L version, on the other hand, uses Vary_VIT_B as its backbone network and is trained on a large-scale formula dataset, showing significant improvements in recognizing complex formulas compared to PP-FormulaNet-S. |
| PP-FormulaNet-L | Inference Model/Training Model | 90.36 | 45.78 | 1482.03 / 1482.03 | - / 3131.54 | 695 | |
| PP-FormulaNet_plus-S | Inference Model/Training Model | 88.71 | 53.32 | 179.20 / 179.20 | - / 260.99 | 248 | PP-FormulaNet_plus is an enhanced version of the formula recognition model developed by the Baidu PaddlePaddle Vision Team, building upon the original PP-FormulaNet. Compared to the original version, PP-FormulaNet_plus utilizes a more diverse formula dataset during training, including sources such as Chinese dissertations, professional books, textbooks, exam papers, and mathematics journals. This expansion significantly improves the model’s recognition capabilities. Among the models, PP-FormulaNet_plus-M and PP-FormulaNet_plus-L have added support for Chinese formulas and increased the maximum number of predicted tokens for formulas from 1,024 to 2,560, greatly enhancing the recognition performance for complex formulas. Meanwhile, the PP-FormulaNet_plus-S model focuses on improving the recognition of English formulas. With these improvements, the PP-FormulaNet_plus series models perform exceptionally well in handling complex and diverse formula recognition tasks. |
| PP-FormulaNet_plus-M | Inference Model/Training Model | 91.45 | 89.76 | 1040.27 / 1040.27 | - / 1615.80 | 592 | |
| PP-FormulaNet_plus-L | Inference Model/Training Model | 92.22 | 90.64 | 1476.07 / 1476.07 | - / 3125.58 | 698 | |
| LaTeX_OCR_rec | Inference Model/Training Model | 74.55 | 39.96 | 1088.89 / 1088.89 | - / - | 99 | LaTeX-OCR is a formula recognition algorithm based on an autoregressive large model. It uses Hybrid ViT as the backbone network and a transformer as the decoder, significantly improving the accuracy of formula recognition. |
Test Environment Description:
- Performance Test Environment
- Test Dataset:
- Document Image Orientation Classification Module: A self-built dataset using PaddleOCR, covering multiple scenarios such as ID cards and documents, containing 1000 images.
- Text Image Rectification Module: DocUNet。
- Layout Region Detection Module: A self-built layout region detection dataset using PaddleOCR, including 500 images of common document types such as Chinese and English papers, magazines, contracts, books, exam papers, and research reports.
- 17-Class Region Detection Model: A self-built layout region detection dataset using PaddleOCR, including 892 images of common document types such as Chinese and English papers, magazines, and research reports.
- Formula Recognition Module: A self-built formula recognition test set using PaddleX.
- Hardware Configuration:
- GPU: NVIDIA Tesla T4
- CPU: Intel Xeon Gold 6271C @ 2.60GHz
- Software Environment:
- Ubuntu 20.04 / CUDA 11.8 / cuDNN 8.9 / TensorRT 8.6.1.6
- paddlepaddle 3.0.0 / paddleocr 3.0.3
- Test Dataset:
- Inference Mode Description
| Mode | GPU Configuration | CPU Configuration | Acceleration Technology Combination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Mode | FP32 Precision / No TRT Acceleration | FP32 Precision / 8 Threads | PaddleInference |
| High-Performance Mode | Optimal combination of pre-selected precision types and acceleration strategies | FP32 Precision / 8 Threads | Pre-selected optimal backend (Paddle/OpenVINO/TRT, etc.) |
If you prioritize model accuracy, choose a model with higher precision; if you care more about inference speed, choose a faster model; if you are concerned about model storage size, choose a smaller model.
2. Quick Start¶
Before using the formula recognition pipeline locally, please ensure that you have completed the wheel package installation according to the installation guide. If you prefer to install dependencies selectively, please refer to the relevant instructions in the installation documentation. The corresponding dependency group for this pipeline is doc-parser. Once installed, you can experience it locally via the command line or integrate it with Python.
Please note: If you encounter issues such as the program becoming unresponsive, unexpected program termination, running out of memory resources, or extremely slow inference during execution, please try adjusting the configuration according to the documentation, such as disabling unnecessary features or using lighter-weight models.
2.1 Command Line Experience¶
You can quickly experience the effect of the formula recognition pipeline with one command. Before running the code below, please download the example image locally:
paddleocr formula_recognition_pipeline -i https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/demo_image/pipelines/general_formula_recognition_001.png
# Specify whether to use the document orientation classification model with --use_doc_orientation_classify.
paddleocr formula_recognition_pipeline -i ./general_formula_recognition_001.png --use_doc_orientation_classify True
# Specify whether to use the text image unwarping module with --use_doc_unwarping.
paddleocr formula_recognition_pipeline -i ./general_formula_recognition_001.png --use_doc_unwarping True
# Specify the use of GPU for model inference with --device.
paddleocr formula_recognition_pipeline -i ./general_formula_recognition_001.png --device gpu
The command line supports more parameter settings. Click to expand for detailed descriptions of the command line parameters.
| Parameter | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
Data to be predicted, required.
Local path of image or PDF file, e.g., /root/data/img.jpg; URL link, e.g., network URL of image or PDF file: Example; Local directory, the directory should contain images to be predicted, e.g., local path: /root/data/ (currently does not support prediction of PDF files in directories; PDF files must be specified with a specific file path).
|
str |
|
save_path |
Specify the path to save the inference results file. If not set, the inference results will not be saved locally. | str |
|
doc_orientation_classify_model_name |
The name of the document orientation classification model. If not set, the default model in pipeline will be used. | str |
|
doc_orientation_classify_model_dir |
The directory path of the document orientation classification model. If not set, the official model will be downloaded. | str |
|
doc_orientation_classify_batch_size |
The batch size of the document orientation classification model. If not set, the default batch size will be set to 1.
|
int |
|
doc_unwarping_model_name |
The name of the text image unwarping model. If not set, the default model in pipeline will be used. | str |
|
doc_unwarping_model_dir |
The directory path of the text image unwarping model. If not set, the official model will be downloaded. | str |
|
doc_unwarping_batch_size |
The batch size of the text image unwarping model. If not set, the default batch size will be set to 1. |
int |
|
use_doc_orientation_classify |
Whether to load and use the document orientation classification module. If not set, the parameter will be set to the value initialized in the pipeline, which is True by default. |
bool |
|
use_doc_unwarping |
Whether to load and use the text image unwarping module. If not set, the parameter will be set to the value initialized in the pipeline, which is True by default. |
bool |
|
layout_detection_model_name |
The name of the layout detection model. If not set, the default model in pipeline will be used. | str |
|
layout_detection_model_dir |
The directory path of the layout detection model. If not set, the official model will be downloaded. | str |
|
layout_threshold |
Score threshold for the layout model. Any value between 0-1. If not set, the default value is used, which is 0.5.
|
float |
|
layout_nms |
Whether to use Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) as post-processing for layout detection. If not set, the parameter will be set to the value initialized in the pipeline, which is True by default.
|
bool |
|
layout_unclip_ratio |
Unclip ratio for detected boxes in layout detection model. Any float > 0. If not set, the default is 1.0.
|
float |
|
layout_merge_bboxes_mode |
The merging mode for the detection boxes output by the model in layout region detection.
large.
|
str |
|
layout_detection_batch_size |
The batch size for the layout region detection model. If not set, the default batch size will be set to 1. |
int |
|
use_layout_detection |
Whether to load and use the layout detection module. If not set, the parameter will be set to the value initialized in the pipeline, which is True by default. |
bool |
|
formula_recognition_model_name |
The name of the formula recognition model. If not set, the default model from the pipeline will be used. | str |
|
formula_recognition_model_dir |
The directory path of the formula recognition model. If not set, the official model will be downloaded. | str |
|
formula_recognition_batch_size |
The batch size for the formula recognition model. If not set, the batch size will default to 1. |
int |
|
device |
The device used for inference. You can specify a particular card number:
|
str |
|
enable_hpi |
Whether to enable the high-performance inference plugin. | bool |
False |
use_tensorrt |
Whether to use the Paddle Inference TensorRT subgraph engine. If the model does not support acceleration through TensorRT, setting this flag will not enable acceleration. For Paddle with CUDA version 11.8, the compatible TensorRT version is 8.x (x>=6), and it is recommended to install TensorRT 8.6.1.6. |
bool |
False |
precision |
Compute precision, such as FP32 or FP16. | str |
fp32 |
enable_mkldnn |
Whether to enable MKL-DNN acceleration for inference. If MKL-DNN is unavailable or the model does not support it, acceleration will not be used even if this flag is set. | bool |
True |
mkldnn_cache_capacity |
MKL-DNN cache capacity. | int |
10 |
cpu_threads |
The number of threads to use when performing inference on the CPU. | int |
8 |
paddlex_config |
Path to PaddleX pipeline configuration file. | str |
The results of running the default configuration of the formula recognition pipeline will be printed to the terminal as follows:
{'res': {'input_path': './general_formula_recognition_001.png', 'page_index': None, 'model_settings': {'use_doc_preprocessor': True, 'use_layout_detection': True}, 'doc_preprocessor_res': {'input_path': None, 'page_index': None, 'model_settings': {'use_doc_orientation_classify': True, 'use_doc_unwarping': True}, 'angle': 0}, 'layout_det_res': {'input_path': None, 'page_index': None, 'boxes': [{'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9855189323425293, 'coordinate': [90.56131, 1086.7773, 658.8992, 1553.2681]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9814704060554504, 'coordinate': [93.04651, 127.988556, 664.8587, 396.60892]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9767388105392456, 'coordinate': [698.4391, 591.0454, 1293.3676, 748.28345]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9712911248207092, 'coordinate': [701.4946, 286.61566, 1299.0099, 391.87457]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9709068536758423, 'coordinate': [697.0126, 751.93604, 1290.2236, 883.64453]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9689271450042725, 'coordinate': [704.01196, 79.645935, 1304.7493, 187.96674]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9683637619018555, 'coordinate': [93.063385, 799.3567, 660.6935, 902.0344]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.9660536646842957, 'coordinate': [728.5045, 440.9215, 1224.0634, 570.8518]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.9616329669952393, 'coordinate': [722.9789, 1333.5085, 1257.1136, 1468.0432]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.9610316753387451, 'coordinate': [756.4525, 1211.323, 1188.0428, 1268.2336]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.960993230342865, 'coordinate': [777.51355, 207.87927, 1222.8966, 267.33014]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9594196677207947, 'coordinate': [697.5154, 957.6764, 1288.6238, 1033.5211]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9593432545661926, 'coordinate': [691.333, 1511.8015, 1282.0968, 1642.5906]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.9589930176734924, 'coordinate': [153.89856, 924.2046, 601.0946, 1036.9038]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9582098722457886, 'coordinate': [87.02347, 1557.2971, 655.9584, 1632.6912]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.9579620957374573, 'coordinate': [810.86975, 1057.0771, 1175.101, 1117.6631]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.9557801485061646, 'coordinate': [165.26271, 557.8495, 598.1803, 614.35]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.953873872756958, 'coordinate': [116.48187, 713.88416, 614.2181, 774.02576]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9521227478981018, 'coordinate': [96.6882, 478.32745, 662.573, 536.5877]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.944242000579834, 'coordinate': [96.12866, 639.1591, 661.7959, 692.4849]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9403323531150818, 'coordinate': [695.9436, 1138.6748, 1286.7242, 1188.0049]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.9249663949012756, 'coordinate': [852.90137, 908.64386, 1131.1882, 933.81793]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.9249223470687866, 'coordinate': [195.28397, 424.81024, 567.697, 451.1291]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'formula_number', 'score': 0.9173304438591003, 'coordinate': [1246.2393, 1079.0535, 1286.3281, 1104.3323]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'formula_number', 'score': 0.9169507026672363, 'coordinate': [1246.9003, 908.6482, 1288.2013, 934.61426]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'formula_number', 'score': 0.915979266166687, 'coordinate': [1247.0374, 1229.1572, 1287.094, 1254.9805]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'formula_number', 'score': 0.9085646867752075, 'coordinate': [1252.864, 492.1079, 1294.6238, 518.47095]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'formula_number', 'score': 0.9017605781555176, 'coordinate': [1242.1719, 1473.6951, 1283.02, 1498.6316]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'formula_number', 'score': 0.8999755382537842, 'coordinate': [1269.8164, 220.34933, 1299.8589, 247.01102]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.8965252041816711, 'coordinate': [96.00711, 235.49493, 295.43823, 265.60016]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.8954343199729919, 'coordinate': [696.85693, 1286.2236, 1083.3921, 1310.8643]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.8952110409736633, 'coordinate': [166.60979, 129.20242, 511.65692, 156.29672]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.893648624420166, 'coordinate': [725.64575, 396.18964, 1263.0391, 422.76813]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'formula_number', 'score': 0.8922948837280273, 'coordinate': [634.14124, 427.77087, 661.1686, 454.10022]}, {'cls_id': 2, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.8892256617546082, 'coordinate': [94.483246, 1058.7595, 441.92313, 1082.4875]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'formula_number', 'score': 0.8878197073936462, 'coordinate': [630.4175, 939.3015, 657.7135, 965.36426]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'formula_number', 'score': 0.8831961154937744, 'coordinate': [630.5835, 1000.95715, 657.4309, 1026.2128]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'formula_number', 'score': 0.8767948150634766, 'coordinate': [634.1024, 575.3833, 660.59094, 601.1677]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.873543918132782, 'coordinate': [95.29655, 1320.3627, 264.93008, 1345.8473]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'formula_number', 'score': 0.8702306151390076, 'coordinate': [633.82825, 730.31525, 659.83215, 755.5485]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.8387619853019714, 'coordinate': [365.19897, 268.29675, 515.7938, 296.07013]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.8314349055290222, 'coordinate': [1090.509, 1599.1382, 1276.6736, 1622.156]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.817135751247406, 'coordinate': [246.175, 161.22958, 314.3764, 186.40591]}, {'cls_id': 3, 'label': 'number', 'score': 0.8042846322059631, 'coordinate': [1297.4036, 7.1497707, 1310.5969, 27.737753]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.7970448136329651, 'coordinate': [538.45593, 478.09354, 661.8812, 508.50778]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.7644855976104736, 'coordinate': [916.51746, 1618.5188, 1009.62537, 1640.8206]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.7423419952392578, 'coordinate': [694.8439, 1612.2507, 861.05334, 1635.9768]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.7072376608848572, 'coordinate': [99.72007, 508.21167, 254.91953, 535.74744]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.6976271867752075, 'coordinate': [696.8011, 1561.4375, 899.79584, 1586.7349]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.6707713007926941, 'coordinate': [1117.0862, 1571.9763, 1191.502, 1594.742]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.6338322162628174, 'coordinate': [577.33484, 1274.4131, 602.5636, 1296.7021]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.6199935674667358, 'coordinate': [175.28284, 349.82376, 241.24683, 376.6708]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.612853467464447, 'coordinate': [773.06287, 595.202, 800.43884, 617.3812]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.6107096672058105, 'coordinate': [706.6776, 316.87082, 736.69714, 339.9352]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.5520269870758057, 'coordinate': [1263.9711, 314.65167, 1292.7728, 337.3896]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.5346108675003052, 'coordinate': [1219.2955, 316.599, 1243.9181, 339.71802]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.5195119380950928, 'coordinate': [254.65729, 323.6553, 326.57758, 349.53494]}, {'cls_id': 7, 'label': 'formula', 'score': 0.501812219619751, 'coordinate': [255.8518, 1350.6472, 301.74304, 1375.5286]}]}, 'formula_res_list': [{'rec_formula': '\\begin{aligned}{\\psi_{0}(M)-\\psi_{}(M,z)=}&{{}\\frac{(1-\\epsilon_{r})}{\\epsilon_{r}}\\frac{\\lambda^{2}c^{2}}{t_{\\operatorname{E}}^{2}\\operatorname{l n}(10)}\\times}\\\\ {}&{{}\\int_{0}^{z}d z^{\\prime}\\frac{d t}{d z^{\\prime}}\\left.\\frac{\\partial\\phi}{\\partial L}\\right|_{L=\\lambda M c^{2}/t_{\\operatorname{E}}},}\\\\ \\end{aligned}', 'formula_region_id': 1, 'dt_polys': ([728.5045, 440.9215, 1224.0634, 570.8518],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\begin{aligned}{p(\\operatorname{l o g}_{10}}&{{}M|\\operatorname{l o g}_{10}\\sigma)=\\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2\\pi}\\epsilon_{0}}}\\\\ {}&{{}\\times\\operatorname{e x p}\\left[-\\frac{1}{2}\\left(\\frac{\\operatorname{l o g}_{10}M-a_{\\bullet}-b_{\\bullet}\\operatorname{l o g}_{10}\\sigma}{\\epsilon_{0}}\\right)^{2}\\right].}\\\\ \\end{aligned}', 'formula_region_id': 2, 'dt_polys': ([722.9789, 1333.5085, 1257.1136, 1468.0432],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\psi_{0}(M)=\\int d\\sigma\\frac{p(\\operatorname{l o g}_{10}M|\\operatorname{l o g}_{10}\\sigma)}{M\\operatorname{l o g}(10)}\\frac{d n}{d\\sigma}(\\sigma),', 'formula_region_id': 3, 'dt_polys': ([756.4525, 1211.323, 1188.0428, 1268.2336],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\phi(L)\\equiv\\frac{d n}{d\\operatorname{l o g}_{10}L}=\\frac{\\phi_{*}}{(L/L_{*})^{\\gamma_{1}}+(L/L_{*})^{\\gamma_{2}}}.', 'formula_region_id': 4, 'dt_polys': ([777.51355, 207.87927, 1222.8966, 267.33014],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\begin{aligned}{\\rho_{\\operatorname{B H}}}&{{}=\\int d M\\psi(M)M}\\\\ {}&{{}=\\frac{1-\\epsilon_{r}}{\\epsilon_{r}c^{2}}\\int_{0}^{\\infty}d z\\frac{d t}{d z}\\int d\\operatorname{l o g}_{10}L\\phi(L,z)L,}\\\\ \\end{aligned}', 'formula_region_id': 5, 'dt_polys': ([153.89856, 924.2046, 601.0946, 1036.9038],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\frac{d n}{d\\sigma}d\\sigma=\\psi_{*}\\left(\\frac{\\sigma}{\\sigma_{*}}\\right)^{\\alpha}\\frac{e^{-(\\sigma/\\sigma_{*})^{\\beta}}}{\\Gamma(\\alpha/\\beta)}\\beta\\frac{d\\sigma}{\\sigma}.', 'formula_region_id': 6, 'dt_polys': ([810.86975, 1057.0771, 1175.101, 1117.6631],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\langle\\dot{M}(M,t)\\rangle\\psi(M,t)=\\frac{(1-\\epsilon_{r})}{\\epsilon_{r}c^{2}\\operatorname{l n}(10)}\\phi(L,t)\\frac{d L}{d M}.', 'formula_region_id': 7, 'dt_polys': ([165.26271, 557.8495, 598.1803, 614.35],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\frac{\\partial\\psi}{\\partial t}(M,t)+\\frac{(1-\\epsilon_{r})}{\\epsilon_{r}}\\frac{\\lambda^{2}c^{2}}{t_{\\operatorname{E}}^{2}\\operatorname{l n}(10)}\\left.\\frac{\\partial\\phi}{\\partial L}\\right|_{L=\\lambda M c^{2}/t_{\\operatorname{E}}}=0,', 'formula_region_id': 8, 'dt_polys': ([116.48187, 713.88416, 614.2181, 774.02576],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\operatorname{l o g}_{10}M=a_{\\bullet}+b_{\\bullet}\\operatorname{l o g}_{10}X.', 'formula_region_id': 9, 'dt_polys': ([852.90137, 908.64386, 1131.1882, 933.81793],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\phi(L,t)d\\operatorname{l o g}_{10}L=\\delta(M,t)\\psi(M,t)d M.', 'formula_region_id': 10, 'dt_polys': ([195.28397, 424.81024, 567.697, 451.1291],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\dot{M}\\:=\\:(1\\:-\\:\\epsilon_{r})\\dot{M}_{\\mathrm{a c c}}^{\\mathrm{~\\tiny~\\cdot~}}', 'formula_region_id': 11, 'dt_polys': ([96.00711, 235.49493, 295.43823, 265.60016],)}, {'rec_formula': 't_{E}=\\sigma_{T}c/4\\pi G m_{p}=4.5\\times10^{8}\\mathrm{y r}', 'formula_region_id': 12, 'dt_polys': ([166.60979, 129.20242, 511.65692, 156.29672],)}, {'rec_formula': 'M_{*}=L_{*}t_{E}/\\tilde{\\lambda}c^{2}', 'formula_region_id': 13, 'dt_polys': ([95.29655, 1320.3627, 264.93008, 1345.8473],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\phi(L,t)d\\operatorname{l o g}_{10}L', 'formula_region_id': 14, 'dt_polys': ([365.19897, 268.29675, 515.7938, 296.07013],)}, {'rec_formula': 'a_{\\bullet}=8.32\\pm0.05', 'formula_region_id': 15, 'dt_polys': ([1090.509, 1599.1382, 1276.6736, 1622.156],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\epsilon_{r}\\dot{M}_{\\mathrm{a c c}}', 'formula_region_id': 16, 'dt_polys': ([246.175, 161.22958, 314.3764, 186.40591],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\langle\\dot{M}(M,t)\\rangle=', 'formula_region_id': 17, 'dt_polys': ([538.45593, 478.09354, 661.8812, 508.50778],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\epsilon_{0}=0.38', 'formula_region_id': 18, 'dt_polys': ([916.51746, 1618.5188, 1009.62537, 1640.8206],)}, {'rec_formula': 'b_{\\bullet}=5.64\\dot{\\pm}\\dot{0.32}', 'formula_region_id': 19, 'dt_polys': ([694.8439, 1612.2507, 861.05334, 1635.9768],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\delta(M,t)\\dot{M}(M,t)', 'formula_region_id': 20, 'dt_polys': ([99.72007, 508.21167, 254.91953, 535.74744],)}, {'rec_formula': 'X=\\sigma/200\\mathrm{k m}\\mathrm{~s^{-1}~}', 'formula_region_id': 21, 'dt_polys': ([696.8011, 1561.4375, 899.79584, 1586.7349],)}, {'rec_formula': 'M-\\sigma', 'formula_region_id': 22, 'dt_polys': ([1117.0862, 1571.9763, 1191.502, 1594.742],)}, {'rec_formula': 'L_{*}', 'formula_region_id': 23, 'dt_polys': ([577.33484, 1274.4131, 602.5636, 1296.7021],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\phi(L,t)', 'formula_region_id': 24, 'dt_polys': ([175.28284, 349.82376, 241.24683, 376.6708],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\psi_{0}', 'formula_region_id': 25, 'dt_polys': ([773.06287, 595.202, 800.43884, 617.3812],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\mathrm{A^{\\prime\\prime}}', 'formula_region_id': 26, 'dt_polys': ([706.6776, 316.87082, 736.69714, 339.9352],)}, {'rec_formula': 'L_{*}', 'formula_region_id': 27, 'dt_polys': ([1263.9711, 314.65167, 1292.7728, 337.3896],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\phi_{*}', 'formula_region_id': 28, 'dt_polys': ([1219.2955, 316.599, 1243.9181, 339.71802],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\delta(M,t)', 'formula_region_id': 29, 'dt_polys': ([254.65729, 323.6553, 326.57758, 349.53494],)}, {'rec_formula': '\\phi(L)', 'formula_region_id': 30, 'dt_polys': ([255.8518, 1350.6472, 301.74304, 1375.5286],)}]}}
The explanation of the running result parameters can refer to the result interpretation in 2.2 Python Script Integration.
The visualization results are saved under save_path, where the visualization result of formula recognition is as follows:
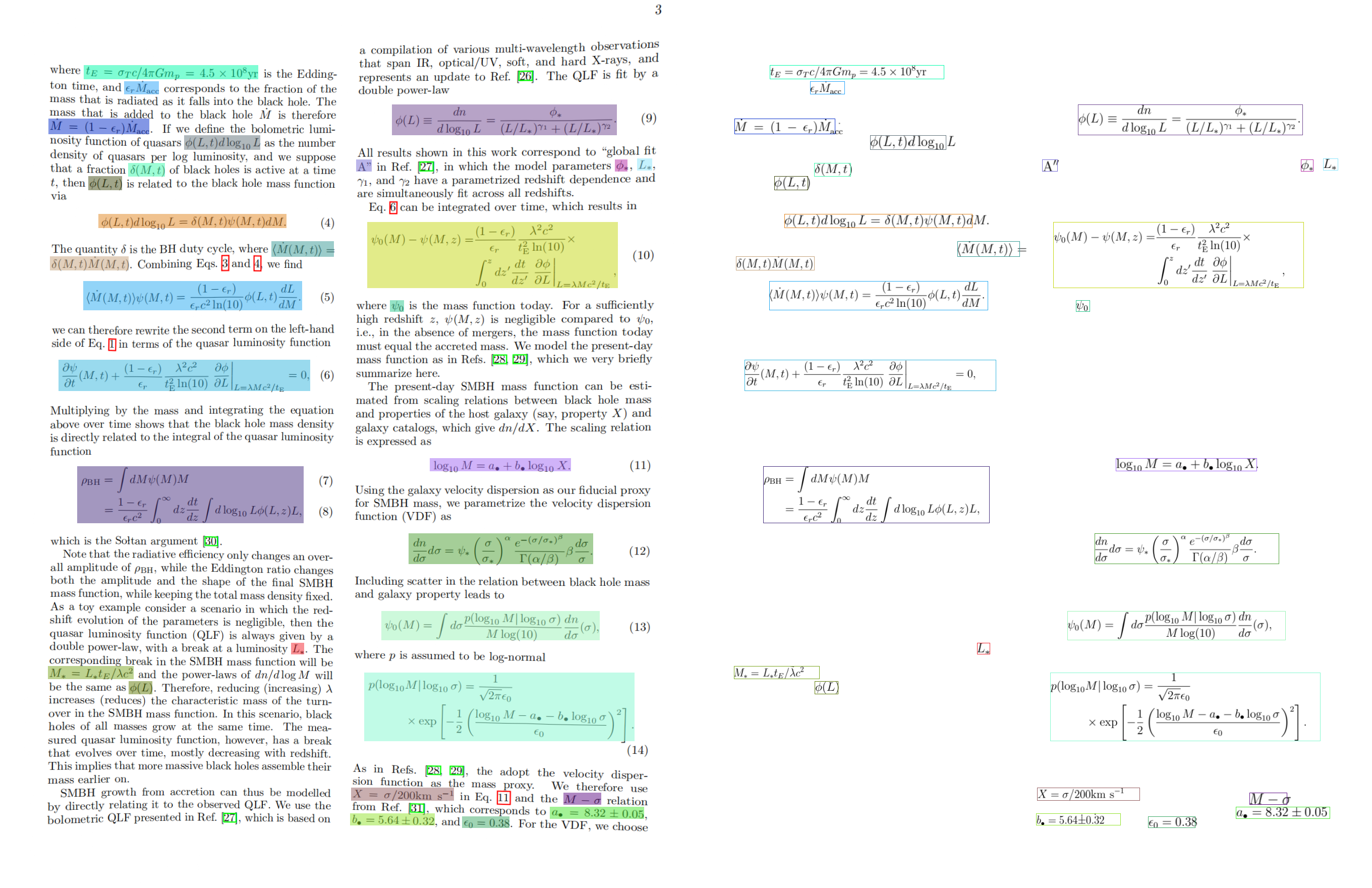
If you need to visualize the formula recognition pipeline, you need to run the following command to install the LaTeX rendering environment. Currently, visualization of the formula recognition pipeline only supports the Ubuntu environment, and other environments are not supported. For complex formulas, the LaTeX result may contain some advanced representations that may not be successfully displayed in environments such as Markdown:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install texlive texlive-latex-base texlive-xetex latex-cjk-all texlive-latex-extra -y
Note: Due to the need to render each formula image during the formula recognition visualization process, the process takes a long time. Please be patient.
2.2 Python Script Integration¶
Using the command line is a quick way to experience and check the results. Generally, in a project, you often need to integrate it through code. You can perform quick inference with just a few lines of code. The inference code is as follows:
from paddleocr import FormulaRecognitionPipeline
pipeline = FormulaRecognitionPipeline()
# ocr = FormulaRecognitionPipeline(use_doc_orientation_classify=True) # Specify whether to use the document orientation classification model with use_doc_orientation_classify.
# ocr = FormulaRecognitionPipeline(use_doc_unwarping=True) # Specify whether to use the text image unwarping module with use_doc_unwarping.
# ocr = FormulaRecognitionPipeline(device="gpu") # Specify the use of GPU for model inference with device.
output = pipeline.predict("./general_formula_recognition_001.png")
for res in output:
res.print() ## Print the structured output of the prediction
res.save_to_img(save_path="output") ## Save the formula visualization result of the current image.
res.save_to_json(save_path="output") ## Save the structured JSON result of the current image
In the above Python script, the following steps are executed:
(1)Instantiate the formula recognition pipeline object through create_pipeline(), with specific parameters as follows:
| Parameter | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
doc_orientation_classify_model_name |
The name of the document orientation classification model. If set to None, the default model in pipeline will be used. |
str|None |
None |
doc_orientation_classify_model_dir |
The directory path of the document orientation classification model. If set to None, the official model will be downloaded. |
str|None |
None |
doc_orientation_classify_batch_size |
The batch size of the document orientation classification model. If set to None, the default batch size will be set to 1. |
int|None |
None |
doc_unwarping_model_name |
The name of the text image unwarping model. If set to None, the default model in pipeline will be used. |
str|None |
None |
doc_unwarping_model_dir |
The directory path of the text image unwarping model. If set to None, the official model will be downloaded. |
str|None |
None |
doc_unwarping_batch_size |
The batch size of the text image unwarping model. If set to None, the default batch size will be set to 1. |
int|None |
None |
use_doc_orientation_classify |
Whether to load and use the document orientation classification module. If set to None, the parameter will be set to the value initialized in the pipeline, which is True by default. |
bool|None |
None |
use_doc_unwarping |
Whether to load and use the text image unwarping module. If set to None, the parameter will be set to the value initialized in the pipeline, which is True by default. |
bool|None |
None |
layout_detection_model_name |
The name of the layout detection model. If set to None, the default model in pipeline will be used. |
str|None |
None |
layout_detection_model_dir |
The directory path of the layout detection model. If set to None, the official model will be downloaded. |
str|None |
None |
layout_threshold |
Threshold for layout detection, used to filter out predictions with low confidence.
|
float|dict|None |
None |
layout_nms |
Whether to use Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) as post-processing for layout detection. If set to None, the parameter will be set to the value initialized in the pipeline, which is set to True by default. |
bool|None |
None |
layout_unclip_ratio |
Expansion factor for the detection boxes of the layout region detection model.
|
float|Tuple[float,float]|dict|None |
None |
layout_merge_bboxes_mode |
Filtering method for overlapping boxes in layout detection.
|
str|dict|None |
None |
layout_detection_batch_size |
The batch size for the layout region detection model. If set to None, the default batch size will be set to 1. |
int|None |
None |
use_layout_detection |
Whether to load and use the layout detection module. If set to None, the parameter will be set to the value initialized in the pipeline, which is True by default. |
bool|None |
None |
formula_recognition_model_name |
The name of the formula recognition model. If set to None, the default model from the pipeline will be used. |
str|None |
None |
formula_recognition_model_dir |
The directory path of the formula recognition model. If set to None, the official model will be downloaded. |
str|None |
None |
formula_recognition_batch_size |
The batch size for the formula recognition model. If set to None, the batch size will default to 1. |
int|None |
None |
device |
The device used for inference. You can specify a particular card number:
|
str|None |
None |
enable_hpi |
Whether to enable the high-performance inference plugin. | bool |
False |
use_tensorrt |
Whether to use the Paddle Inference TensorRT subgraph engine. If the model does not support acceleration through TensorRT, setting this flag will not enable acceleration. For Paddle with CUDA version 11.8, the compatible TensorRT version is 8.x (x>=6), and it is recommended to install TensorRT 8.6.1.6. |
bool |
False |
precision |
Compute precision, such as FP32 or FP16. | str |
"fp32" |
enable_mkldnn |
Whether to enable MKL-DNN acceleration for inference. If MKL-DNN is unavailable or the model does not support it, acceleration will not be used even if this flag is set. | bool |
True |
mkldnn_cache_capacity |
MKL-DNN cache capacity. | int |
10 |
cpu_threads |
The number of threads to use when performing inference on the CPU. | int |
8 |
paddlex_config |
Path to PaddleX pipeline configuration file. | str|None |
None |
(2)Call the predict() method of the formula recognition pipeline object to perform inference prediction. This method will return a list of results.
Additionally, the pipeline also provides the predict_iter() method. Both methods are completely consistent in terms of parameter acceptance and result return. The difference is that predict_iter() returns a generator, which allows for step-by-step processing and retrieval of prediction results. This is suitable for handling large datasets or scenarios where memory saving is desired. You can choose to use either of these methods based on your actual needs.
Here are the parameters of the predict() method and their descriptions:
| Parameter | Description | Type | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
Data to be predicted, supporting multiple input types, required.
|
Python Var|str|list |
|
use_layout_detection |
Whether to use the layout detection module during inference. | bool|None |
None |
use_doc_orientation_classify |
Whether to use the document orientation classification module during inference. | bool|None |
None |
use_doc_unwarping |
Whether to use the text image unwarping module during inference. | bool|None |
None |
layout_threshold |
Same meaning as the instantiation parameters. If set to None, the instantiation value is used; otherwise, this parameter takes precedence. |
float|dict|None |
None |
layout_nms |
Same meaning as the instantiation parameters. If set to None, the instantiation value is used; otherwise, this parameter takes precedence. |
bool|None |
None |
layout_unclip_ratio |
Same meaning as the instantiation parameters. If set to None, the instantiation value is used; otherwise, this parameter takes precedence. |
float|Tuple[float,float]|dict|None |
None |
layout_merge_bboxes_mode |
Same meaning as the instantiation parameters. If set to None, the instantiation value is used; otherwise, this parameter takes precedence. |
string |
None |
(3)Process the prediction results, where the prediction result for each sample corresponds to a Result object, and supports operations such as printing, saving as an image, and saving as a json file:
| Method | Description | Parameter | Parameter Type | Parameter Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
print() |
Print results to terminal | format_json |
bool |
Whether to format the output content using JSON indentation. |
True |
indent |
int |
Specify the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable. Effective only when format_json is True. |
4 | ||
ensure_ascii |
bool |
Control whether to escape non-ASCII characters to Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False retains the original characters. Effective only when format_json is True. |
False |
||
save_to_json() |
Save results as a JSON file | save_path |
str |
Path to save the file. If it is a directory, the saved file will be named the same as the input file type. | 无 |
indent |
int |
Specify the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable. Effective only when format_json is True. |
4 | ||
ensure_ascii |
bool |
Control whether to escape non-ASCII characters to Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False retains the original characters. Effective only when format_json is True. |
False |
||
save_to_img() |
Save results as an image file | save_path |
str |
Path to save the file, supports directory or file path. | 无 |
-
Calling the
print()method will print the results to the terminal. The content printed to the terminal is explained as follows:-
input_path:(str)The input path of the image to be predicted. -
page_index:(Union[int, None])If the input is a PDF file, this indicates the current page number of the PDF. Otherwise, it isNone -
model_settings:(Dict[str, bool])The model parameters required for the pipeline configuration.use_doc_preprocessor:(bool)Controls whether to enable the document preprocessing sub-pipeline.use_layout_detection:(bool)Controls whether to enable the layout area detection module.
-
doc_preprocessor_res:(Dict[str, Union[str, Dict[str, bool], int]])The output result of the document preprocessing sub-pipeline. It exists only whenuse_doc_preprocessor=True.input_path:(Union[str, None])The image path accepted by the image preprocessing sub-pipeline. When the input is anumpy.ndarray, it is saved asNone.model_settings:(Dict)The model configuration parameters of the preprocessing sub-pipeline.use_doc_orientation_classify:(bool)Controls whether to enable document orientation classification.use_doc_unwarping:(bool)Controls whether to enable document distortion correction.
angle:(int)The prediction result of document orientation classification. When enabled, it takes values from [0,1,2,3], corresponding to [0°,90°,180°,270°]; when disabled, it is -1.
layout_det_res:(Dict[str, List[Dict]])The output result of the layout area detection module. It exists only whenuse_layout_detection=True.input_path:(Union[str, None])The image path accepted by the layout area detection module. When the input is anumpy.ndarray, it is saved asNone.boxes:(List[Dict[int, str, float, List[float]]])A list of layout area detection prediction results.cls_id:(int)The class ID predicted by layout area detection.label:(str)The class label predicted by layout area detection.score:(float)The confidence score of the predicted class.coordinate:(List[float])The bounding box coordinates predicted by layout area detection, in the format [x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max], where (x_min, y_min) is the top-left corner and (x_max, y_max) is the bottom-right corner.
formula_res_list:(List[Dict[str, int, List[float]]])A list of formula recognition prediction results.rec_formula:(str)The LaTeX source code predicted by formula recognition.formula_region_id:(int)The ID number predicted by formula recognition.dt_polys:(List[float])The bounding box coordinates predicted by formula recognition, in the format [x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max], where (x_min, y_min) is the top-left corner and (x_max, y_max) is the bottom-right corner.
-
-
Calling the
save_to_json()method will save the above content to the specifiedsave_path. If a directory is specified, the saved path will besave_path/{your_img_basename}_res.json. If a file is specified, it will be saved directly to that file. Since JSON files do not support saving numpy arrays,numpy.arraytypes will be converted to list format. -
Calling the
save_to_img()method will save the visualization results to the specifiedsave_path. If a directory is specified, the saved path will besave_path/{your_img_basename}_formula_res_img.{your_img_extension}. If a file is specified, it will be saved directly to that file. (The pipeline usually contains many result images, so it is not recommended to specify a specific file path directly, otherwise multiple images will be overwritten and only the last one will be retained.) -
In addition, you can also obtain the visualization image with results and the prediction results through attributes, as follows:
| Attribute | Attribute Description |
|---|---|
json |
Get the prediction results in json format |
img |
Get the visualization image in dict format |
- The prediction result obtained from the
jsonattribute is of the dict type, and its content is consistent with what is saved by calling thesave_to_json()method. - The prediction result returned by the
imgattribute is a dictionary-type data. The keys arepreprocessed_img、layout_det_resandformula_res_img, and the corresponding values are threeImage.Imageobjects: the first one is used to display the visualization of image preprocessing, the second one is for displaying the visualization of layout region detection, and the third one is for displaying the visualization of formula recognition. If the image preprocessing submodule is not used, the dictionary will not contain thepreprocessed_imgkey. Similarly, if the layout region detection submodule is not used, the dictionary will not contain thelayout_det_reskey.
3. Development Integration/Deployment¶
If the formula recognition pipeline meets your requirements for inference speed and accuracy, you can proceed directly with development integration/deployment.
If you need to integrate the formula recognition pipeline into your Python project, you can refer to the example code in 2.2 Python Script Integration.
In addition, PaddleOCR also provides two other deployment methods, which are detailed as follows:
🚀 High-Performance Inference: In real-world production environments, many applications have stringent standards for performance metrics of deployment strategies, particularly regarding response speed, to ensure efficient system operation and a smooth user experience. To address this, PaddleOCR offers high-performance inference capabilities designed to deeply optimize the performance of model inference and pre/post-processing, significantly accelerating the end-to-end process. For detailed information on the high-performance inference process, please refer to the High-Performance Inference Guide.
☁️ Service-Based Deployment: Service-Based Deployment is a common deployment form in real-world production environments. By encapsulating inference capabilities as a service, clients can access these services via network requests to obtain inference results. For detailed instructions on Service-Based Deployment in pipelines, please refer to the Service-Based Deployment Guide.
Below are the API references for basic service-based deployment and multi-language service invocation examples:
API Reference
For the main operations provided by the service:
- The HTTP request method is POST.
- Both the request body and response body are JSON data (JSON objects).
- When the request is processed successfully, the response status code is
200, and the attributes of the response body are as follows:
| Name | Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
logId |
string |
The UUID of the request. |
errorCode |
integer |
Error code. Fixed as 0. |
errorMsg |
string |
Error message. Fixed as "Success". |
result |
object |
The result of the operation. |
- When the request is not processed successfully, the attributes of the response body are as follows:
| Name | Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
logId |
string |
The UUID of the request. |
errorCode |
integer |
Error code. Same as the response status code. |
errorMsg |
string |
Error message. |
The main operations provided by the service are as follows:
infer
Obtain the formula recognition results from images.
POST /formula-recognition
- The attributes of the request body are as follows:
| Name | Type | Meaning | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
file |
string |
The URL of an image or PDF file accessible by the server, or the Base64-encoded content of the file. By default, for PDF files exceeding 10 pages, only the first 10 pages will be processed. To remove the page limit, please add the following configuration to the pipeline configuration file: |
Yes |
fileType |
integer | null |
The type of the file. 0 for PDF files, 1 for image files. If this attribute is missing, the file type will be inferred from the URL. |
No |
useDocOrientationClassify |
boolean | null |
Please refer to the description of the use_doc_orientation_classify parameter of the pipeline object's predict method. |
No |
useDocUnwarping |
boolean | null |
Please refer to the description of the use_doc_unwarping parameter of the pipeline object's predict method. |
No |
useLayoutDetection |
boolean | null |
Please refer to the description of the use_layout_detection parameter of the pipeline object's predict method. |
No |
layoutThreshold |
number | null |
Please refer to the description of the layout_threshold parameter of the pipeline object's predict method. |
No |
layoutNms |
boolean | null |
Please refer to the description of the layout_nms parameter of the pipeline object's predict method. |
No |
layoutUnclipRatio |
number | array | null |
Please refer to the description of the layout_unclip_ratio parameter of the pipeline object's predict method. |
No |
layoutMergeBboxesMode |
string | null |
Please refer to the description of the layout_merge_bboxes_mode parameter of the pipeline object's predict method. |
No |
visualize |
boolean | null |
Whether to return the final visualization image and intermediate images during the processing.
For example, adding the following setting to the pipeline config file: visualize parameter in the request.If neither the request body nor the configuration file is set (If visualize is set to null in the request and not defined in the configuration file), the image is returned by default.
|
No |
- When the request is processed successfully, the
resultin the response body has the following attributes:
| 名称 | 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
formulaRecResults |
object |
The formula recognition results. The array length is 1 (for image input) or the actual number of document pages processed (for PDF input). For PDF input, each element in the array represents the result of each page actually processed in the PDF file. |
dataInfo |
object |
Information about the input data. |
Each element in formulaRecResults is an object with the following attributes:
| Name | Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
prunedResult |
object |
A simplified version of the res field in the JSON representation of the result generated by the pipeline object's predict method, excluding the input_path and the page_index fields. |
outputImages |
object | null |
See the description of the img attribute of the result of the pipeline prediction. The images are in JPEG format and are Base64-encoded. |
inputImage | null |
string |
The input image. The image is in JPEG format and is Base64-encoded. |
Multi-language Service Invocation Example
Python
import base64
import requests
API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/formula-recognition"
file_path = "./demo.jpg"
with open(file_path, "rb") as file:
file_bytes = file.read()
file_data = base64.b64encode(file_bytes).decode("ascii")
payload = {"file": file_data, "fileType": 1}
response = requests.post(API_URL, json=payload)
assert response.status_code == 200
result = response.json()["result"]
for i, res in enumerate(result["formulaRecResults"]):
print(res["prunedResult"])
for img_name, img in res["outputImages"].items():
img_path = f"{img_name}_{i}.jpg"
with open(img_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(base64.b64decode(img))
print(f"Output image saved at {img_path}")
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include "cpp-httplib/httplib.h" // https://github.com/Huiyicc/cpp-httplib
#include "nlohmann/json.hpp" // https://github.com/nlohmann/json
#include "base64.hpp" // https://github.com/tobiaslocker/base64
int main() {
httplib::Client client("localhost", 8080);
const std::string filePath = "./demo.jpg";
std::ifstream file(filePath, std::ios::binary | std::ios::ate);
if (!file) {
std::cerr << "Error opening file: " << filePath << std::endl;
return 1;
}
std::streamsize size = file.tellg();
file.seekg(0, std::ios::beg);
std::vector buffer(size);
if (!file.read(buffer.data(), size)) {
std::cerr << "Error reading file." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
std::string bufferStr(buffer.data(), static_cast(size));
std::string encodedFile = base64::to_base64(bufferStr);
nlohmann::json jsonObj;
jsonObj["file"] = encodedFile;
jsonObj["fileType"] = 1;
auto response = client.Post("/formula-recognition", jsonObj.dump(), "application/json");
if (response && response->status == 200) {
nlohmann::json jsonResponse = nlohmann::json::parse(response->body);
auto result = jsonResponse["result"];
if (!result.is_object() || !result["formulaRecResults"].is_array()) {
std::cerr << "Unexpected response format." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < result["formulaRecResults"].size(); ++i) {
auto res = result["formulaRecResults"][i];
if (res.contains("prunedResult")) {
std::cout << "Recognized formula: " << res["prunedResult"].dump() << std::endl;
}
if (res.contains("outputImages") && res["outputImages"].is_object()) {
for (auto& [imgName, imgData] : res["outputImages"].items()) {
std::string outputPath = imgName + "_" + std::to_string(i) + ".jpg";
std::string decodedImage = base64::from_base64(imgData.get());
std::ofstream outFile(outputPath, std::ios::binary);
if (outFile.is_open()) {
outFile.write(decodedImage.c_str(), decodedImage.size());
outFile.close();
std::cout << "Saved image: " << outputPath << std::endl;
} else {
std::cerr << "Failed to write image: " << outputPath << std::endl;
}
}
}
}
} else {
std::cerr << "Request failed." << std::endl;
if (response) {
std::cerr << "HTTP status: " << response->status << std::endl;
std::cerr << "Response body: " << response->body << std::endl;
}
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
Java
import okhttp3.*;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.ObjectNode;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Base64;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/formula-recognition";
String imagePath = "./demo.jpg";
File file = new File(imagePath);
byte[] fileContent = java.nio.file.Files.readAllBytes(file.toPath());
String base64Image = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(fileContent);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
ObjectNode payload = objectMapper.createObjectNode();
payload.put("file", base64Image);
payload.put("fileType", 1);
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
MediaType JSON = MediaType.get("application/json; charset=utf-8");
RequestBody body = RequestBody.create(JSON, payload.toString());
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(API_URL)
.post(body)
.build();
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
String responseBody = response.body().string();
JsonNode root = objectMapper.readTree(responseBody);
JsonNode result = root.get("result");
JsonNode formulaRecResults = result.get("formulaRecResults");
for (int i = 0; i < formulaRecResults.size(); i++) {
JsonNode item = formulaRecResults.get(i);
int finalI = i;
JsonNode prunedResult = item.get("prunedResult");
System.out.println("Pruned Result [" + i + "]: " + prunedResult.toString());
JsonNode outputImages = item.get("outputImages");
if (outputImages != null && outputImages.isObject()) {
outputImages.fieldNames().forEachRemaining(imgName -> {
try {
String imgBase64 = outputImages.get(imgName).asText();
byte[] imgBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(imgBase64);
String imgPath = imgName + "_" + finalI + ".jpg";
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(imgPath)) {
fos.write(imgBytes);
System.out.println("Saved image: " + imgPath);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Failed to save image: " + e.getMessage());
}
});
}
}
} else {
System.err.println("Request failed with HTTP code: " + response.code());
}
}
}
}
Go
package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"os"
)
func main() {
API_URL := "http://localhost:8080/formula-recognition"
filePath := "./demo.jpg"
fileBytes, err := ioutil.ReadFile(filePath)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error reading file: %v\n", err)
return
}
fileData := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(fileBytes)
payload := map[string]interface{}{
"file": fileData,
"fileType": 1,
}
payloadBytes, err := json.Marshal(payload)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error marshaling payload: %v\n", err)
return
}
client := &http.Client{}
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", API_URL, bytes.NewBuffer(payloadBytes))
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error creating request: %v\n", err)
return
}
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
res, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error sending request: %v\n", err)
return
}
defer res.Body.Close()
if res.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
fmt.Printf("Unexpected status code: %d\n", res.StatusCode)
return
}
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error reading response body: %v\n", err)
return
}
type FormulaRecResult struct {
PrunedResult map[string]interface{} `json:"prunedResult"`
OutputImages map[string]string `json:"outputImages"`
InputImage *string `json:"inputImage"`
}
type Response struct {
Result struct {
FormulaRecResults []FormulaRecResult `json:"formulaRecResults"`
DataInfo interface{} `json:"dataInfo"`
} `json:"result"`
}
var respData Response
if err := json.Unmarshal(body, &respData); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error unmarshaling response: %v\n", err)
return
}
for i, res := range respData.Result.FormulaRecResults {
fmt.Printf("Result %d - prunedResult: %+v\n", i, res.PrunedResult)
for imgName, imgData := range res.OutputImages {
imgBytes, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(imgData)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error decoding image %s_%d: %v\n", imgName, i, err)
continue
}
filename := fmt.Sprintf("%s_%d.jpg", imgName, i)
if err := os.WriteFile(filename, imgBytes, 0644); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error saving image %s: %v\n", filename, err)
continue
}
fmt.Printf("Saved image to %s\n", filename)
}
}
}
C#
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Newtonsoft.Json.Linq;
class Program
{
static readonly string API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/formula-recognition";
static readonly string inputFilePath = "./demo.jpg";
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
var httpClient = new HttpClient();
byte[] fileBytes = File.ReadAllBytes(inputFilePath);
string fileData = Convert.ToBase64String(fileBytes);
var payload = new JObject
{
{ "file", fileData },
{ "fileType", 1 }
};
var content = new StringContent(payload.ToString(), Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
HttpResponseMessage response = await httpClient.PostAsync(API_URL, content);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
string responseBody = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
JObject jsonResponse = JObject.Parse(responseBody);
JArray formulaRecResults = (JArray)jsonResponse["result"]["formulaRecResults"];
for (int i = 0; i < formulaRecResults.Count; i++)
{
var res = formulaRecResults[i];
Console.WriteLine($"[{i}] prunedResult:\n{res["prunedResult"]}");
JObject outputImages = res["outputImages"] as JObject;
if (outputImages != null)
{
foreach (var img in outputImages)
{
string imgName = img.Key;
string base64Img = img.Value?.ToString();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(base64Img))
{
string imgPath = $"{imgName}_{i}.jpg";
byte[] imageBytes = Convert.FromBase64String(base64Img);
File.WriteAllBytes(imgPath, imageBytes);
Console.WriteLine($"Output image saved at {imgPath}");
}
}
}
}
}
}
Node.js
const axios = require('axios');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const API_URL = 'http://localhost:8080/formula-recognition';
const inputFilePath = './demo.jpg';
const fileType = 1;
function encodeImageToBase64(filePath) {
const bitmap = fs.readFileSync(filePath);
return Buffer.from(bitmap).toString('base64');
}
const payload = {
file: encodeImageToBase64(inputFilePath),
fileType: fileType
};
axios.post(API_URL, payload)
.then((response) => {
const resultArray = response.data.result.formulaRecResults;
resultArray.forEach((res, index) => {
console.log(`\n[${index}] prunedResult:`);
console.log(res.prunedResult);
const outputImages = res.outputImages;
if (outputImages) {
Object.entries(outputImages).forEach(([imgName, base64Img]) => {
const outputPath = `${imgName}_${index}.jpg`;
fs.writeFileSync(outputPath, Buffer.from(base64Img, 'base64'));
console.log(`Saved output image: ${outputPath}`);
});
} else {
console.log(`[${index}] outputImages is null`);
}
});
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error('API error:', error.message);
});
PHP
<?php
$API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/formula-recognition";
$image_path = "./demo.jpg";
$image_data = base64_encode(file_get_contents($image_path));
$payload = array("file" => $image_data, "fileType" => 1);
$ch = curl_init($API_URL);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, json_encode($payload));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, array('Content-Type: application/json'));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
$response = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
$result = json_decode($response, true)["result"]["formulaRecResults"];
foreach ($result as $i => $item) {
echo "[$i] prunedResult:\n";
print_r($item["prunedResult"]);
if (!empty($item["outputImages"])) {
foreach ($item["outputImages"] as $img_name => $base64_img) {
$img_path = "{$img_name}_{$i}.jpg";
file_put_contents($img_path, base64_decode($base64_img));
echo "Output image saved at $img_path\n";
}
} else {
echo "No outputImages found for item $i\n";
}
}
?>
4. Custom Development¶
If the default model weights provided by the formula recognition pipeline do not meet your requirements in terms of accuracy or speed, you can try to fine-tune the existing models using your own domain-specific or application-specific data to improve the recognition performance of the formula recognition pipeline in your scenario.
4.1 Model Fine-Tuning¶
Since the formula recognition pipeline consists of several modules, if the pipeline's performance is not satisfactory, the issue may arise from any one of these modules. You can analyze the poorly recognized images to determine which module is problematic and refer to the corresponding fine-tuning tutorial links in the table below for model fine-tuning.
| Scenario | Fine-Tuning Module | Reference Link |
|---|---|---|
| Formulas are missing | Layout Detection Module | Link |
| Formula content is inaccurate | Formula Recognition Module | Link |
| Whole-image rotation correction is inaccurate | Document Image Orientation Classification Module | Link |
| Image distortion correction is inaccurate | Text Image Correction Module | Fine-tuning not supported |
4.2 Model Deployment¶
After you complete fine-tuning training using a private dataset, you can obtain a local model weight file. You can then use the fine-tuned model weights by specifying the local model save path through parameters or by customizing the pipeline configuration file.
4.2.1 Specify the local model path through parameters¶
When initializing the pipeline object, specify the local model path through parameters. Take the usage of the weights after fine-tuning the text detection model as an example, as follows:
Command line mode:
# Specify the local model path via --formula_recognition_model_dir
paddleocr formula_recognition_pipeline -i ./general_formula_recognition_001.png --formula_recognition_model_dir your_formula_recognition_model_path
# PP-FormulaNet_plus-M model is used as the default formula recognition model. If you do not fine-tune this model, modify the model name by using --formula_recognition_model_name
paddleocr formula_recognition_pipeline -i ./general_formula_recognition_001.png --formula_recognition_model_name PP-FormulaNet_plus-M --formula_recognition_model_dir your_ppformulanet_plus-m_formula_recognition_model_path
Script mode:
from paddleocr import FormulaRecognitionPipeline
# Specify the local model path via formula_recognition_model_dir
pipeline = FormulaRecognitionPipeline(formula_recognition_model_dir="./your_formula_recognition_model_path")
output = pipeline.predict("./general_formula_recognition_001.png")
for res in output:
res.print() ## Print the structured output of the prediction
res.save_to_img(save_path="output") ## Save the formula visualization result of the current image.
res.save_to_json(save_path="output") ## Save the structured JSON result of the current image
# PP-FormulaNet_plus-M model is used as the default formula recognition model. If you do not fine-tune this model, modify the model name by using formula_recognition_model_name
# pipeline = FormulaRecognitionPipeline(formula_recognition_model_name="PP-FormulaNet_plus-M", formula_recognition_model_dir="./your_ppformulanet_plus-m_formula_recognition_model_path")
4.2.2 Specify the local model path through the configuration file¶
1.Obtain the pipeline configuration file
Call the export_paddlex_config_to_yaml method of the Formula Recognition Pipeline object in PaddleOCR to export the current pipeline configuration as a YAML file:
from paddleocr import FormulaRecognitionPipeline
pipeline = FormulaRecognitionPipeline()
pipeline.export_paddlex_config_to_yaml("FormulaRecognitionPipeline.yaml")
2.Modify the Configuration File
After obtaining the default pipeline configuration file, replace the paths of the default model weights with the local paths of your fine-tuned model weights. For example:
......
SubModules:
FormulaRecognition:
batch_size: 5
model_dir: null # Replace with the path to your fine-tuned formula recognition model weights
model_name: PP-FormulaNet_plus-M # If the name of the fine-tuned model is different from the default model name, please modify it here as well
module_name: formula_recognition
LayoutDetection:
batch_size: 1
layout_merge_bboxes_mode: large
layout_nms: true
layout_unclip_ratio: 1.0
model_dir: null # Replace with the path to your fine-tuned layout detection model weights
model_name: PP-DocLayout_plus-L # If the name of the fine-tuned model is different from the default model name, please modify it here as well
module_name: layout_detection
threshold: 0.5
SubPipelines:
DocPreprocessor:
SubModules:
DocOrientationClassify:
batch_size: 1
model_dir: null # Replace with the path to your fine-tuned document image orientation classification model weights
model_name: PP-LCNet_x1_0_doc_ori # If the name of the fine-tuned model is different from the default model name, please modify it here as well
module_name: doc_text_orientation
DocUnwarping:
batch_size: 1
model_dir: null
model_name: UVDoc
module_name: image_unwarping
pipeline_name: doc_preprocessor
use_doc_orientation_classify: true
use_doc_unwarping: true
pipeline_name: formula_recognition
use_doc_preprocessor: true
use_layout_detection: true
......
The pipeline configuration file includes not only the parameters supported by the PaddleOCR CLI and Python API but also advanced configurations. For detailed instructions, refer to the PaddleX Pipeline Usage Overview and adjust the configurations as needed.
3.Load the Configuration File in CLI
After modifying the configuration file, specify its path using the --paddlex_config parameter in the command line. PaddleOCR will read the file and apply the configurations. Example:
paddleocr formula_recognition_pipeline -i ./general_formula_recognition_001.png --paddlex_config FormulaRecognitionPipeline.yaml
When initializing the pipeline object, pass the path of the PaddleX pipeline configuration file or a configuration dictionary via the paddlex_config parameter. PaddleOCR will read and apply the configurations. Example:
from paddleocr import FormulaRecognitionPipeline
pipeline = FormulaRecognitionPipeline(paddlex_config="FormulaRecognitionPipeline.yaml")
output = pipeline.predict("./general_formula_recognition_001.png")
for res in output:
res.print() ## Print the structured output of the prediction
res.save_to_img(save_path="output") ## Save the formula visualization result of the current image.
res.save_to_json(save_path="output") ## Save the structured JSON result of the current image