Table Cell Detection Module Usage Tutorial¶
I. Overview¶
The Table Cell Detection Module is a key component of the table recognition task, responsible for locating and marking each cell region in table images. The performance of this module directly affects the accuracy and efficiency of the entire table recognition process. The Table Cell Detection Module typically outputs bounding boxes for each cell region, which are then passed as input to the table recognition pipeline for further processing.
II. Supported Model List¶
| Model | Model Download Link | mAP(%) | GPU Inference Time (ms) [Regular Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
CPU Inference Time (ms) [Regular Mode / High-Performance Mode] |
Model Storage Size (M) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-DETR-L_wired_table_cell_det | Inference Model/Training Model | 82.7 | 35.00 / 10.45 | 495.51 / 495.51 | 124M | RT-DETR is a real-time end-to-end object detection model. The Baidu PaddlePaddle Vision team pre-trained on a self-built table cell detection dataset based on the RT-DETR-L as the base model, achieving good performance in detecting both wired and wireless table cells. |
| RT-DETR-L_wireless_table_cell_det | Inference Model/Training Model |
Test Environment Description:
- Performance Test Environment
- Test Dataset: Internal evaluation set built by PaddleX.
- Hardware Configuration:
- GPU: NVIDIA Tesla T4
- CPU: Intel Xeon Gold 6271C @ 2.60GHz
- Other Environment: Ubuntu 20.04 / cuDNN 8.6 / TensorRT 8.5.2.2
- Inference Mode Explanation
| Mode | GPU Configuration | CPU Configuration | Acceleration Technology Combination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Mode | FP32 Precision / No TRT Acceleration | FP32 Precision / 8 Threads | PaddleInference |
| High-Performance Mode | Optimal combination of prior precision type and acceleration strategy | FP32 Precision / 8 Threads | Choose the optimal prior backend (Paddle/OpenVINO/TRT, etc.) |
III. Quick Start¶
❗ Before starting quickly, please first install the PaddleOCR wheel package. For details, please refer to the installation tutorial.
You can quickly experience it with one command:
paddleocr table_cells_detection -i https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/table_recognition.jpg
You can also integrate model inference from the table cell detection module into your project. Before running the following code, please download the sample image locally.
from paddleocr import TableCellsDetection
model = TableCellsDetection(model_name="RT-DETR-L_wired_table_cell_det")
output = model.predict("table_recognition.jpg", threshold=0.3, batch_size=1)
for res in output:
res.print(json_format=False)
res.save_to_img("./output/")
res.save_to_json("./output/res.json")
After running, the result obtained is:
{'res': {'input_path': 'table_recognition.jpg', 'page_index': None, 'boxes': [{'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'cell', 'score': 0.9698355197906494, 'coordinate': [2.3011515, 0, 546.29926, 30.530712]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'cell', 'score': 0.9690820574760437, 'coordinate': [212.37508, 64.62493, 403.58868, 95.61413]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'cell', 'score': 0.9668057560920715, 'coordinate': [212.46791, 30.311079, 403.7182, 64.62613]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'cell', 'score': 0.966505229473114, 'coordinate': [403.56082, 64.62544, 546.83215, 95.66117]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'cell', 'score': 0.9662341475486755, 'coordinate': [109.48873, 64.66485, 212.5177, 95.631294]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'cell', 'score': 0.9654079079627991, 'coordinate': [212.39197, 95.63037, 403.60852, 126.78792]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'cell', 'score': 0.9653300642967224, 'coordinate': [2.2320926, 64.62229, 109.600494, 95.59732]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'cell', 'score': 0.9639787673950195, 'coordinate': [403.5752, 30.562355, 546.98975, 64.61531]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'cell', 'score': 0.9636150002479553, 'coordinate': [2.1537683, 30.410172, 109.568306, 64.62762]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'cell', 'score': 0.9631900191307068, 'coordinate': [2.0534437, 95.57448, 109.57601, 126.71458]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'cell', 'score': 0.9631181359291077, 'coordinate': [403.65976, 95.68139, 546.84766, 126.713394]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'cell', 'score': 0.9614537358283997, 'coordinate': [109.56504, 30.391184, 212.65425, 64.6444]}, {'cls_id': 0, 'label': 'cell', 'score': 0.9607433080673218, 'coordinate': [109.525795, 95.62622, 212.44917, 126.8258]}]}}
The parameter meanings are as follows:
input_path: Path of the input image to be predictedpage_index: If the input is a PDF file, it indicates which page of the PDF it is; otherwise, it isNoneboxes: Predicted bounding box information, a list of dictionaries. Each dictionary represents a detected object and contains the following information:cls_id: Class ID, an integerlabel: Class label, a stringscore: Confidence of the bounding box, a floatcoordinate: Coordinates of the bounding box, a list of floats in the format[xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax]
The visualized image is as follows:
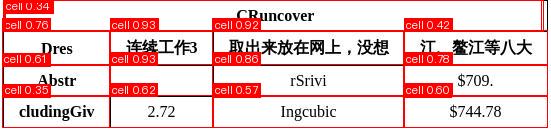
The relevant methods, parameters, etc., are described as follows:
TableCellsDetectioninstantiates the table cell detection model (takingRT-DETR-L_wired_table_cell_detas an example here), with specific explanations as follows:
| Parameter | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
model_name |
Model name | str |
PP-DocLayout-L |
model_dir |
Model storage path | str |
None |
device |
Device(s) to use for inference. Examples: cpu, gpu, npu, gpu:0, gpu:0,1.If multiple devices are specified, inference will be performed in parallel. Note that parallel inference is not always supported. By default, GPU 0 will be used if available; otherwise, the CPU will be used. |
str |
None |
enable_hpi |
Whether to use the high performance inference. | bool |
False |
use_tensorrt |
Whether to use the Paddle Inference TensorRT subgraph engine. | bool |
False |
min_subgraph_size |
Minimum subgraph size for TensorRT when using the Paddle Inference TensorRT subgraph engine. | int |
3 |
precision |
Precision for TensorRT when using the Paddle Inference TensorRT subgraph engine. Options: fp32, fp16, etc. |
str |
fp32 |
enable_mkldnn |
Whether to use MKL-DNN acceleration for inference. | bool |
True |
cpu_threads |
Number of threads to use for inference on CPUs. | int |
10 |
img_size |
Size of the input image;If not specified, the default configuration of the PaddleOCR official model will be used Examples:
|
int/list/None |
None |
threshold |
Threshold to filter out low-confidence predictions; In table cell detection tasks, lowering the threshold appropriately may help to obtain more accurate results. Examples:
|
float/dict/None |
None |
-
Among them,
model_namemust be specified. After specifyingmodel_name, the default model parameters built into PaddleX are used. Whenmodel_diris specified, the user-defined model is used. -
Call the
predict()method of the table cell detection model for inference prediction. This method will return a result list. Additionally, this module also provides apredict_iter()method. Both methods are consistent in terms of parameter acceptance and result return. The difference is thatpredict_iter()returns agenerator, which can process and obtain prediction results step by step, suitable for handling large datasets or scenarios where memory saving is desired. You can choose to use either of these methods according to your actual needs. Thepredict()method has parametersinput,batch_size, andthreshold, with specific explanations as follows:
| Parameter | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
Input data to be predicted. Required. Supports multiple input types:
|
Python Var|str|list |
|
batch_size |
Batch size, positive integer. | int |
1 |
threshold |
Threshold for filtering out low-confidence prediction results; Examples:
|
float/dict/None |
None |
- Process the prediction results. The prediction result for each sample is a corresponding Result object, which supports printing, saving as an image, and saving as a
jsonfile:
| Method | Description | Parameter | Type | Parameter Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
print() |
Print result to terminal | format_json |
bool |
Whether to format the output content using JSON indentation |
True |
indent |
int |
Specifies the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable, effective only when format_json is True |
4 | ||
ensure_ascii |
bool |
Controls whether to escape non-ASCII characters into Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False will retain the original characters, effective only when format_json is True |
False |
||
save_to_json() |
Save the result as a json format file | save_path |
str |
The path to save the file. When specified as a directory, the saved file is named consistent with the input file type. | None |
indent |
int |
Specifies the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable, effective only when format_json is True |
4 | ||
ensure_ascii |
bool |
Controls whether to escape non-ASCII characters into Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False will retain the original characters, effective only when format_json is True |
False |
||
save_to_img() |
Save the result as an image format file | save_path |
str |
The path to save the file. When specified as a directory, the saved file is named consistent with the input file type. | None |
- Additionally, the result can be obtained through attributes that provide the visualized images with results and the prediction results, as follows:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
json |
Get the prediction result in json format |
img |
Get the visualized image |
IV. Secondary Development¶
Since PaddleOCR does not directly provide training for the table cell detection module, if you need to train a table cell detection model, you can refer to the PaddleX Table Cell Detection Module Secondary Development section for training. The trained model can be seamlessly integrated into the PaddleOCR API for inference.