Text Recognition Module Development Tutorial¶
I. Overview¶
The text recognition module is the core component of an OCR (Optical Character Recognition) system, responsible for extracting text information from text regions within images. The performance of this module directly impacts the accuracy and efficiency of the entire OCR system. The text recognition module typically receives bounding boxes of text regions output by the text detection module as input. Through complex image processing and deep learning algorithms, it converts the text in images into editable and searchable electronic text. The accuracy of text recognition results is crucial for subsequent applications such as information extraction and data mining.
II. Supported Model List¶
| Model | Model Download Link | Recognition Avg Accuracy(%) | GPU Inference Time (ms) | CPU Inference Time (ms) | Model Size (M) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec | Inference Model/Trained Model | 78.20 | 7.95018 | 46.7868 | 10.6 M | PP-OCRv4, developed by Baidu's PaddlePaddle Vision Team, is the next version of the PP-OCRv3 text recognition model. By introducing data augmentation schemes, GTC-NRTR guidance branches, and other strategies, it further improves text recognition accuracy without compromising model inference speed. The model offers both server and mobile versions to meet industrial needs in different scenarios. |
| PP-OCRv4_server_rec | Inference Model/Trained Model | 79.20 | 7.19439 | 140.179 | 71.2 M |
Note: The evaluation set for the above accuracy metrics is PaddleOCR's self-built Chinese dataset, covering street scenes, web images, documents, handwriting, and more, with 1.1w images for text recognition. GPU inference time for all models is based on an NVIDIA Tesla T4 machine with FP32 precision. CPU inference speed is based on an Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 5117 CPU @ 2.00GHz with 8 threads and FP32 precision.
❗ The above list features the 2 core models that the text recognition module primarily supports. In total, this module supports 4 models. The complete list of models is as follows:
👉Model List Details
| Model | Model Download Link | Recognition Avg Accuracy(%) | GPU Inference Time (ms) | CPU Inference Time (ms) | Model Size (M) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec | Inference Model/Trained Model | 78.20 | 7.95018 | 46.7868 | 10.6 M | PP-OCRv4, developed by Baidu's PaddlePaddle Vision Team, is the next version of the PP-OCRv3 text recognition model. By introducing data augmentation schemes, GTC-NRTR guidance branches, and other strategies, it further improves text recognition accuracy without compromising model inference speed. The model offers both server and mobile versions to meet industrial needs in different scenarios. |
| PP-OCRv4_server_rec | Inference Model/Trained Model | 79.20 | 7.19439 | 140.179 | 71.2 M |
Note: The evaluation set for the above accuracy metrics is PaddleOCR's self-built Chinese dataset, covering street scenes, web images, documents, handwriting, and more, with 1.1w images for text recognition. GPU inference time for all models is based on an NVIDIA Tesla T4 machine with FP32 precision. CPU inference speed is based on an Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 5117 CPU @ 2.00GHz with 8 threads and FP32 precision.
| Model | Model Download Link | Recognition Avg Accuracy(%) | GPU Inference Time (ms) | CPU Inference Time | Model Size (M) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ch_SVTRv2_rec | Inference Model/Trained Model | 68.81 | 8.36801 | 165.706 | 73.9 M | SVTRv2, a server-side text recognition model developed by the OpenOCR team at the Vision and Learning Lab (FVL) of Fudan University, also won first place in the OCR End-to-End Recognition Task of the PaddleOCR Algorithm Model Challenge. Its A-rank end-to-end recognition accuracy is 6% higher than PP-OCRv4. |
Note: The evaluation set for the above accuracy metrics is the OCR End-to-End Recognition Task of the PaddleOCR Algorithm Model Challenge - Track 1 A-rank. GPU inference time for all models is based on an NVIDIA Tesla T4 machine with FP32 precision. CPU inference speed is based on an Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 5117 CPU @ 2.00GHz with 8 threads and FP32 precision.
| Model | Model Download Link | Recognition Avg Accuracy(%) | GPU Inference Time (ms) | CPU Inference Time | Model Size (M) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ch_RepSVTR_rec | Inference Model/Trained Model | 65.07 | 10.5047 | 51.5647 | 22.1 M | RepSVTR, a mobile text recognition model based on SVTRv2, won first place in the OCR End-to-End Recognition Task of the PaddleOCR Algorithm Model Challenge. Its B-rank end-to-end recognition accuracy is 2.5% higher than PP-OCRv4, with comparable inference speed. |
Note: The evaluation set for the above accuracy metrics is the OCR End-to-End Recognition Task of the PaddleOCR Algorithm Model Challenge - Track 1 B-rank. GPU inference time for all models is based on an NVIDIA Tesla T4 machine with FP32 precision. CPU inference speed is based on an Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 5117 CPU @ 2.00GHz with 8 threads and FP32 precision.
III. Quick Integration¶
Before quick integration, you need to install the PaddleX wheel package. For the installation method, please refer to the PaddleX Local Installation Tutorial. After installing the wheel package, a few lines of code can complete the inference of the text recognition module. You can switch models under this module freely, and you can also integrate the model inference of the text recognition module into your project.
Before running the following code, please download the demo image to your local machine.
from paddlex import create_model
model = create_model("PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec")
output = model.predict("general_ocr_rec_001.png", batch_size=1)
for res in output:
res.print(json_format=False)
res.save_to_img("./output/")
res.save_to_json("./output/res.json")
IV. Custom Development¶
If you are seeking higher accuracy from existing models, you can use PaddleX's custom development capabilities to develop better text recognition models. Before using PaddleX to develop text recognition models, please ensure that you have installed the relevant model training plugins for OCR in PaddleX. The installation process can be found in the custom development section of the PaddleX Local Installation Guide.
4.1 Data Preparation¶
Before model training, it is necessary to prepare the corresponding dataset for each task module. PaddleX provides a data validation function for each module, and only data that passes the validation can be used for model training. Additionally, PaddleX offers Demo datasets for each module, allowing you to complete subsequent development based on the officially provided Demo data. If you wish to use a private dataset for subsequent model training, you can refer to the PaddleX Text Detection/Text Recognition Task Module Data Annotation Tutorial.
4.1.1 Download Demo Data¶
You can use the following commands to download the Demo dataset to a specified folder:
wget https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/data/ocr_rec_dataset_examples.tar -P ./dataset
tar -xf ./dataset/ocr_rec_dataset_examples.tar -C ./dataset/
4.1.2 Data Validation¶
A single command can complete data validation:
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/text_recognition/PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=check_dataset \
-o Global.dataset_dir=./dataset/ocr_rec_dataset_examples
Check dataset passed ! in the log. The validation results file is saved in ./output/check_dataset_result.json, and related outputs are saved in the ./output/check_dataset directory in the current directory, including visual examples of sample images and sample distribution histograms.
👉 Validation Result Details (Click to Expand)
The specific content of the validation result file is:
{
"done_flag": true,
"check_pass": true,
"attributes": {
"train_samples": 4468,
"train_sample_paths": [
"../dataset/ocr_rec_dataset_examples/images/train_word_1.png",
"../dataset/ocr_rec_dataset_examples/images/train_word_10.png"
],
"val_samples": 2077,
"val_sample_paths": [
"../dataset/ocr_rec_dataset_examples/images/val_word_1.png",
"../dataset/ocr_rec_dataset_examples/images/val_word_10.png"
]
},
"analysis": {
"histogram": "check_dataset/histogram.png"
},
"dataset_path": "./dataset/ocr_rec_dataset_examples",
"show_type": "image",
"dataset_type": "MSTextRecDataset"
}
In the above validation result, check_pass being true indicates that the dataset format meets the requirements. Explanations for other indicators are as follows:
attributes.train_samples: The number of training set samples in this dataset is 4468;attributes.val_samples: The number of validation set samples in this dataset is 2077;attributes.train_sample_paths: A list of relative paths to the visualized training set samples in this dataset;attributes.val_sample_paths: A list of relative paths to the visualized validation set samples in this dataset; Additionally, the dataset validation also analyzes the distribution of character length ratios in the dataset and generates a distribution histogram (histogram.png):
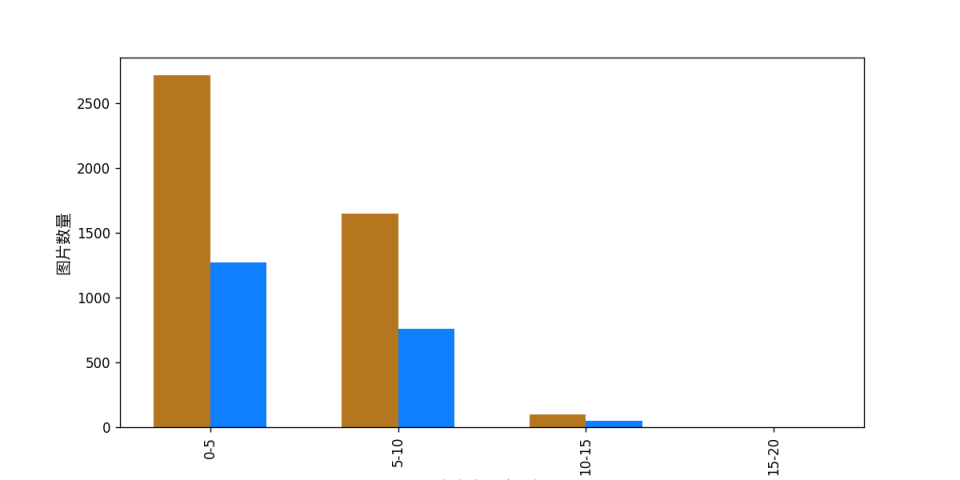
4.1.3 Dataset Format Conversion/Dataset Splitting (Optional)¶
After completing data validation, you can convert the dataset format or re-split the training/validation ratio of the dataset by modifying the configuration file or appending hyperparameters.
👉 Dataset Format Conversion/Dataset Splitting Details (Click to Expand)
(1) Dataset Format Conversion
Text recognition does not currently support data conversion.
(2) Dataset Splitting
The parameters for dataset splitting can be set by modifying the CheckDataset section in the configuration file. Examples of some parameters in the configuration file are as follows:
CheckDataset:split:enable: Whether to re-split the dataset. Set toTrueto enable dataset splitting, default isFalse;train_percent: If re-splitting the dataset, set the percentage of the training set. The type is any integer between 0-100, and it must sum up to 100 withval_percent; For example, if you want to re-split the dataset with a 90% training set and a 10% validation set, modify the configuration file as follows:
......
CheckDataset:
......
split:
enable: True
train_percent: 90
val_percent: 10
......
Then execute the command:
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/text_recognition/PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=check_dataset \
-o Global.dataset_dir=./dataset/ocr_rec_dataset_examples
After data splitting, the original annotation files will be renamed to xxx.bak in the original path.
The above parameters also support setting through appending command line arguments:
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/text_recognition/PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=check_dataset \
-o Global.dataset_dir=./dataset/ocr_rec_dataset_examples \
-o CheckDataset.split.enable=True \
-o CheckDataset.split.train_percent=90 \
-o CheckDataset.split.val_percent=10
4.2 Model Training¶
Model training can be completed with a single command. Here's an example of training the PP-OCRv4 mobile text recognition model (PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec):
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/text_recognition/PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=train \
-o Global.dataset_dir=./dataset/ocr_rec_dataset_examples
- Specify the path to the model's
.yamlconfiguration file (here it'sPP-OCRv4_mobile_rec.yaml,When training other models, you need to specify the corresponding configuration files. The relationship between the model and configuration files can be found in the PaddleX Model List (CPU/GPU)) - Specify the mode as model training:
-o Global.mode=train - Specify the path to the training dataset:
-o Global.dataset_dir. Other related parameters can be set by modifying theGlobalandTrainfields in the.yamlconfiguration file or adjusted by appending parameters in the command line. For example, to specify training on the first 2 GPUs:-o Global.device=gpu:0,1; to set the number of training epochs to 10:-o Train.epochs_iters=10. For more modifiable parameters and their detailed explanations, refer to the PaddleX Common Configuration File Parameters.
👉 More Information (Click to Expand)
- During model training, PaddleX automatically saves the model weight files, with the default being
output. If you need to specify a save path, you can set it through the-o Global.outputfield in the configuration file. - PaddleX shields you from the concepts of dynamic graph weights and static graph weights. During model training, both dynamic and static graph weights are produced, and static graph weights are selected by default for model inference.
-
After completing the model training, all outputs are saved in the specified output directory (default is
./output/), typically including: -
train_result.json: Training result record file, recording whether the training task was completed normally, as well as the output weight metrics, related file paths, etc.; train.log: Training log file, recording changes in model metrics and loss during training;config.yaml: Training configuration file, recording the hyperparameter configuration for this training session;.pdparams,.pdema,.pdopt.pdstate,.pdiparams,.pdmodel: Model weight-related files, including network parameters, optimizer, EMA, static graph network parameters, static graph network structure, etc.;
4.3 Model Evaluation¶
After completing model training, you can evaluate the specified model weights file on the validation set to verify the model's accuracy. Using PaddleX for model evaluation can be done with a single command:
```bash
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/text_recognition/PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=evaluate \
-o Global.dataset_dir=./dataset/ocr_rec_dataset_examples
- Specify the
.yamlconfiguration file path for the model (here it'sPP-OCRv4_mobile_rec.yaml) - Specify the mode as model evaluation:
-o Global.mode=evaluate - Specify the path to the validation dataset:
-o Global.dataset_dirOther related parameters can be set by modifying theGlobalandEvaluatefields in the.yamlconfiguration file. For details, refer to PaddleX Common Model Configuration File Parameter Description.
👉 More Information (Click to Expand)
When evaluating the model, you need to specify the model weights file path. Each configuration file has a default weight save path. If you need to change it, simply append the command line parameter to set it, such as -o Evaluate.weight_path=./output/best_model/best_model.pdparams.
After completing the model evaluation, an evaluate_result.json file will be produced, which records the evaluation results, specifically, whether the evaluation task was completed successfully and the model's evaluation metrics, including acc、norm_edit_dis;
4.4 Model Inference and Model Integration¶
After completing model training and evaluation, you can use the trained model weights for inference prediction or Python integration.
4.4.1 Model Inference¶
To perform inference prediction via the command line, simply use the following command:
Before running the following code, please download the demo image to your local machine.
python main.py -c paddlex/configs/text_recognition/PP-OCRv4_mobile_rec.yaml \
-o Global.mode=predict \
-o Predict.model_dir="./output/best_accuracy/inference" \
-o Predict.input="general_ocr_rec_001.png"
- Specify the
.yamlconfiguration file path for the model (here it isPP-OCRv4_mobile_rec.yaml) - Specify the mode as model inference prediction:
-o Global.mode=predict - Specify the model weights path:
-o Predict.model_dir="./output/best_accuracy/inference" - Specify the input data path:
-o Predict.input="..."Other related parameters can be set by modifying theGlobalandPredictfields in the.yamlconfiguration file. For details, refer to PaddleX Common Model Configuration File Parameter Description.
4.4.2 Model Integration¶
Models can be directly integrated into the PaddleX pipelines or into your own projects.
1.Pipeline Integration
The text recognition module can be integrated into PaddleX pipelines such as the General OCR Pipeline, General Table Recognition Pipeline, and Document Scene Information Extraction Pipeline v3 (PP-ChatOCRv3). Simply replace the model path to update the text recognition module of the relevant pipeline.
2.Module Integration
The weights you produce can be directly integrated into the text recognition module. Refer to the Quick Integration Python example code. Simply replace the model with the path to your trained model.